Home /
Expert Answers /
Mechanical Engineering /
water-flows-steadily-within-a-pipe-at-constant-density-1000kg-m3-three-locations-are-marked-pa993
(Solved): Water flows steadily within a pipe at constant density =1000kg/m3. Three locations are marked ...
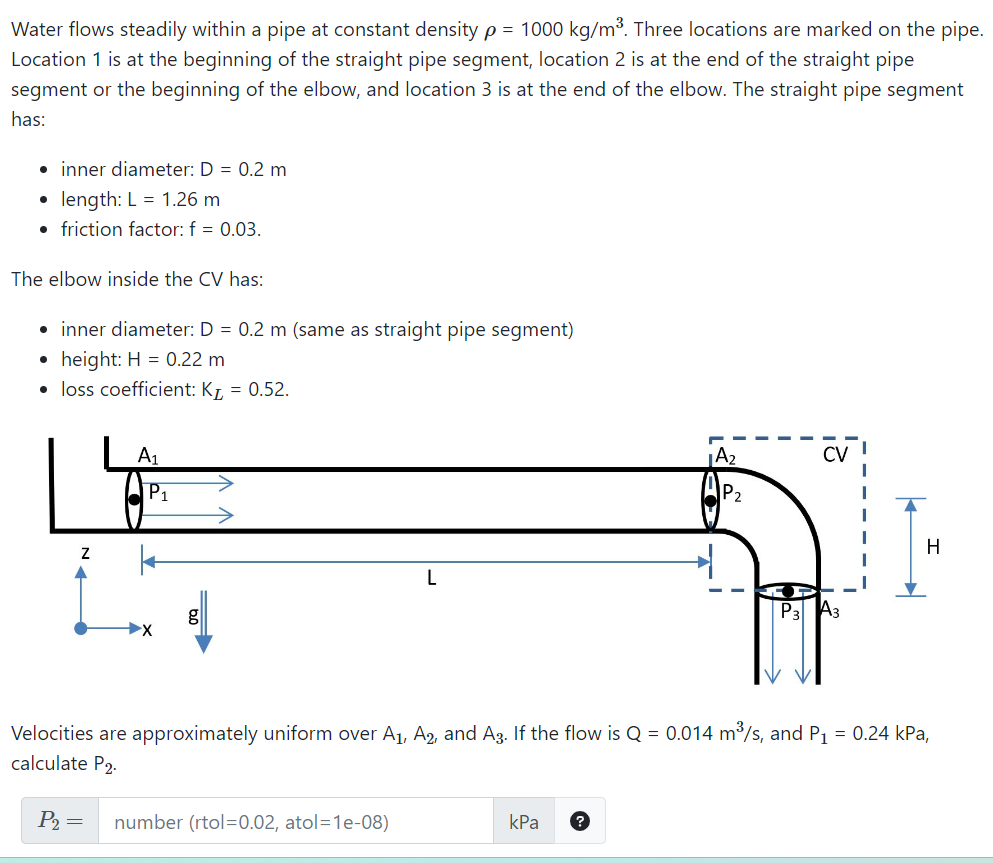
Water flows steadily within a pipe at constant density . Three locations are marked on the pipe. Location 1 is at the beginning of the straight pipe segment, location 2 is at the end of the straight pipe segment or the beginning of the elbow, and location 3 is at the end of the elbow. The straight pipe segment has: - inner diameter: - length: - friction factor: . The elbow inside the CV has: - inner diameter: (same as straight pipe segment) - height: - loss coefficient: . Velocities are approximately uniform over and . If the flow is , and , calculate .
Expert Answer
To solve this problem, we can apply the Bernoulli's equation along a streamline between locations 1 and 2, and then between locations 2 and 3. Since the flow is steady and incompressible, the mass flow rate through any cross section of the pipe is constant. Therefore, we can equate the mass flow rates at locations 1 and 3: where ? is the density of water, Q is the volume flow rate, A1 and A3 are the cross-sectional areas of the pipe at locations 1 and 3, respectively, and V1 and V3 are the velocities of the water at those locations.From the problem statement, we know that the velocity is approximately uniform over A1, A2, and Ag. Therefore, we can assume that V1 = V2 and V2 = V3. Using the equation of continuity, we can then write:A2 = A1 = A3 = Q/V2Next, we can apply the Bernoulli's equation between locations 1 and 2, and then between locations 2 and 3.