Home /
Expert Answers /
Trigonometry /
use-the-law-of-sines-to-find-the-indicated-side-x-assume-a-17-round-your-answer-to-pa607
(Solved): Use the Law of Sines to find the indicated side \( x \). (Assume \( a=17 \). Round your answer to ...
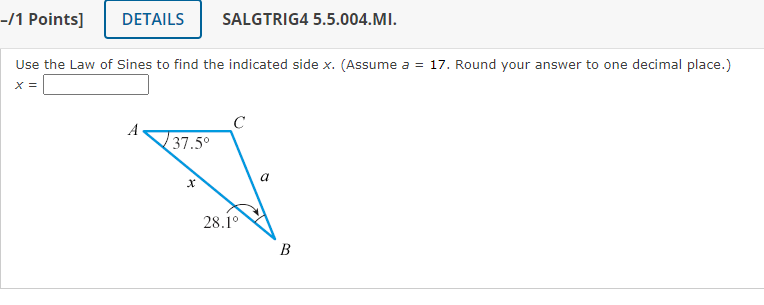
Use the Law of Sines to find the indicated side \( x \). (Assume \( a=17 \). Round your answer to one decimal place.) \[ x= \]
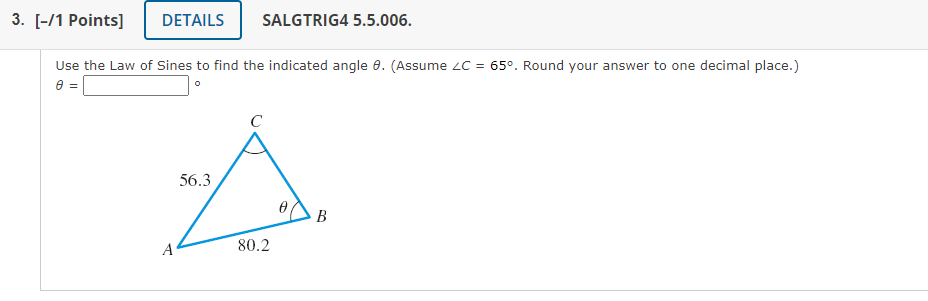
Use the Law of Sines to find the indicated angle \( \theta \). (Assume \( \angle C=65^{\circ} \). Round your answer to one decimal place.) \( \theta= \)
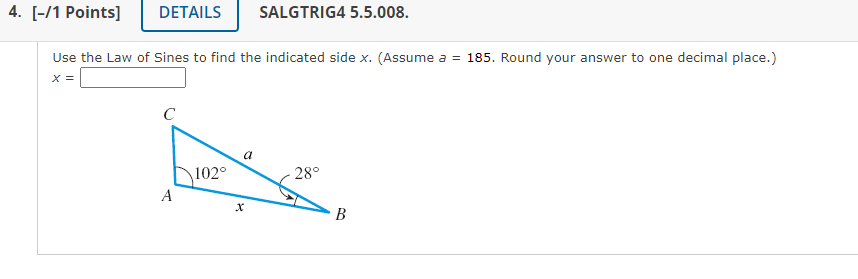
Use the Law of Sines to find the indicated side \( x \). (Assume \( a=185 \). Round your answer to one decimal place.) \[ x= \]
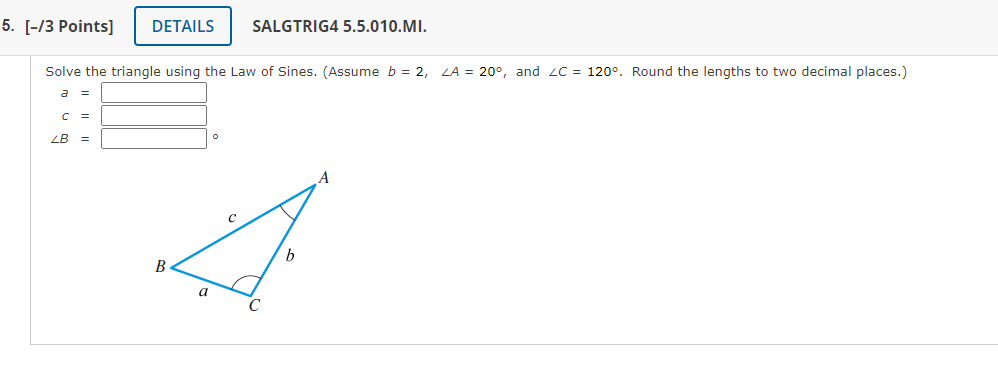
Solve the triangle using the Law of Sines. (Assume \( b=2, \angle A=20^{\circ} \), and \( \angle C=120^{\circ} \). Round the lengths to two decimal places.) \[ \begin{aligned} a &=\\ c &=\\ \angle B &= \end{aligned} \]
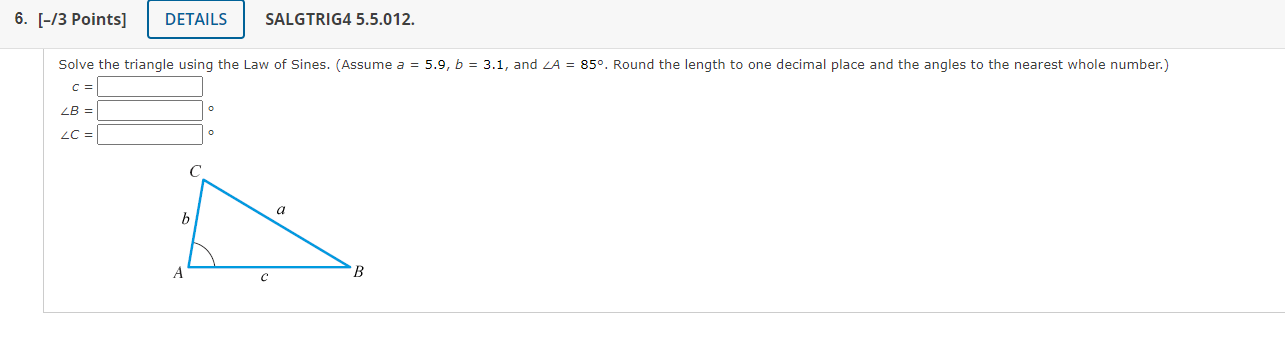
Solve the triangle using the Law of Sines. (Assume \( a=5.9, b=3.1 \), and \( \angle A=85^{\circ} \). Round the length to one decimal place and the angles to the nearest whole number.) \( c= \) \[ \angle B=\quad \circ \] \[ \angle C=\quad \quad \circ \]
Sketch the triangle. \[ \angle A=25^{\circ}, \quad \angle B=95^{\circ}, \quad C=70 \] Solve the triangle using the Law of Sines. (Round side lengths to one decimal place.) \( a= \) \[ b= \] \[ \angle C= \]
\[ \angle A=24^{\circ}, \quad \angle B=110^{\circ}, \quad a=450 \] Solve the triangle using the Law of Sines. (Round side lengths to one decimal place.) \[ b= \] \[ c=1 \] \[ \angle C= \]
Sketch the triangle. \[ \angle B=12^{\circ}, \quad \angle C=99^{\circ}, \quad C=105 \] Solve the triangle using the Law of Sines. (Round side lengths to the nearest integer.) \[ \begin{aligned} a &=\\ b &=\\ \angle A &= \end{aligned} \]
0. [-/6 Points \( ] \) SALGTRIG4 5.5.020.MI. \( a=31, \quad c=46, \quad \angle A=31^{\circ} \)
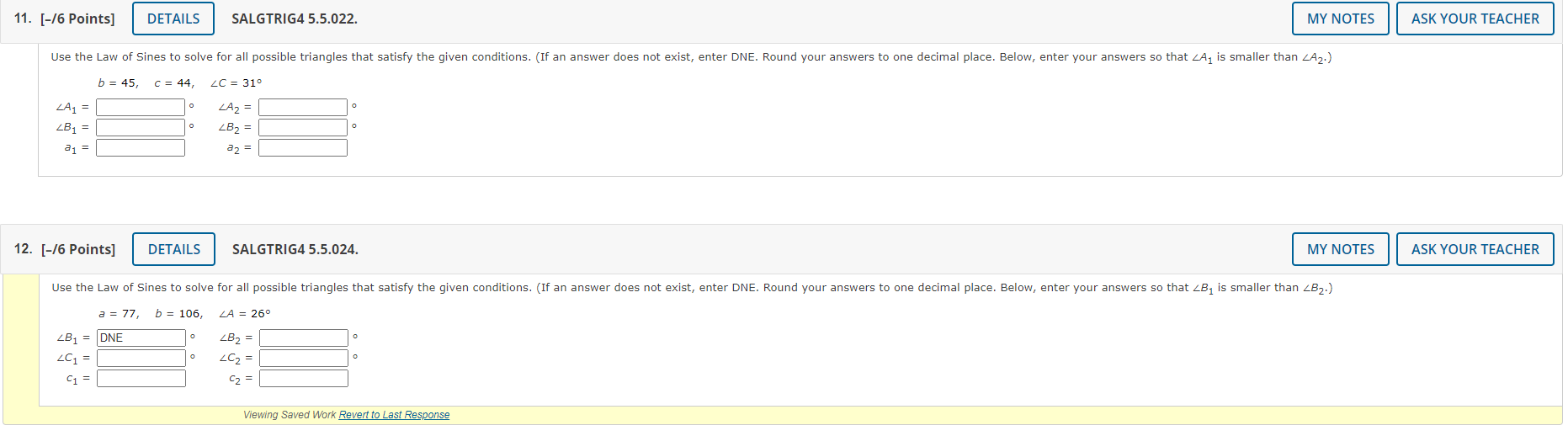
\( b=45, \quad c=44, \quad \angle C=31^{\circ} \) \begin{tabular}{l|ll|l} \( \angle A_{1}= \) & \( 1 \circ \) & \( \angle A_{2}= \) & \\ \( \angle B_{1}= \) & \( \circ \) & \( \angle B_{2}= \) & \( \circ \) \end{tabular} [-/6 Points] \( \quad \) SALGTRIG4 5.5.024. \( a=77, \quad b=106, \quad \angle A=26^{\circ} \)
Expert Answer
1) A = 37.5° B = 28.1° a = 17 As sum of all angles of a tria
![Sketch the triangle.
\[
\angle A=25^{\circ}, \quad \angle B=95^{\circ}, \quad C=70
\]
Solve the triangle using the Law of Sin](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/522/52260561-c3e6-4f8e-970d-5448a9686294/phpRF2knK)
![\[
\angle A=24^{\circ}, \quad \angle B=110^{\circ}, \quad a=450
\]
Solve the triangle using the Law of Sines. (Round side len](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/0bd/0bd8b6c0-8351-4b8f-b885-592d7cedc4bc/phpMe9Gup)
![Sketch the triangle.
\[
\angle B=12^{\circ}, \quad \angle C=99^{\circ}, \quad C=105
\]
Solve the triangle using the Law of Si](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/d92/d92a2f90-4da0-4677-a27a-7fa6a3ca00dd/phpPsTKQE)
![0. [-/6 Points \( ] \)
SALGTRIG4 5.5.020.MI.
\( a=31, \quad c=46, \quad \angle A=31^{\circ} \)](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/eb6/eb675907-394f-40ef-aceb-64a257108739/php3r4v8c)