(Solved): This lab has 3 parts. attached is the default template which needs changing along with the main.cpp ...
This lab has 3 parts. attached is the default template which needs changing along with the main.cpp which does not change.
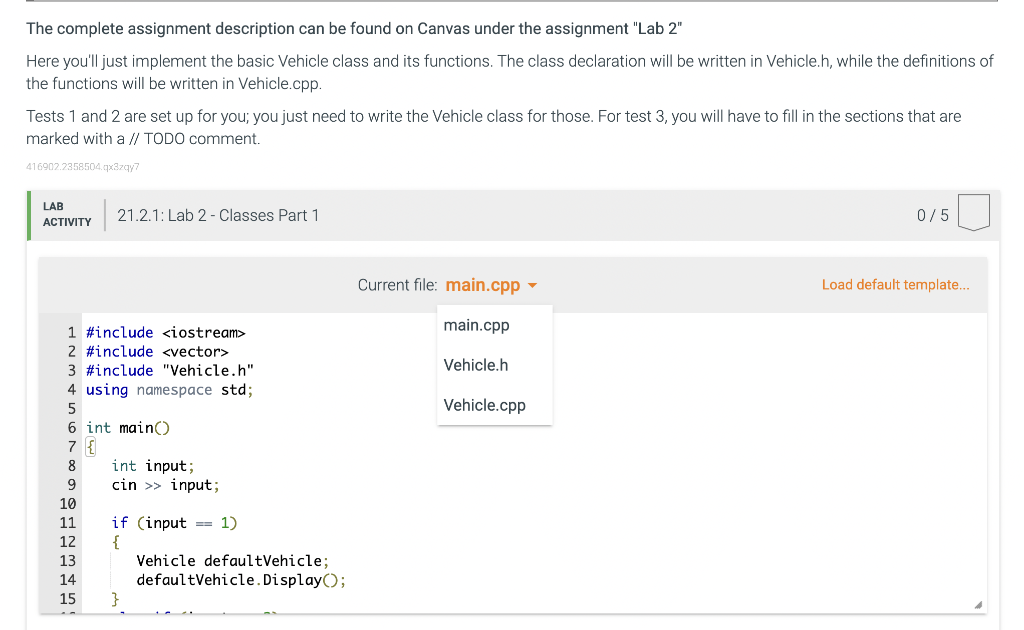
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "Vehicle.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int input;
cin >> input;
if (input == 1)
{
Vehicle defaultVehicle;
defaultVehicle.Display();
}
else if (input == 2)
{
Vehicle customVehicle1("Tesla", "Model S",
2019, 46122, 42);
customVehicle1.Display();
Vehicle customVehicle2("Chrysler", "New
Yorker", 1984, 2000, 100423);
customVehicle2.Display();
}
else if (input == 3)
{
Vehicle customVehicle1("Chrysler", "New
Yorker", 1984, 2000, 100423);
Vehicle customVehicle2("COP3503", "Moped",
2019, 2200, 45);
cout << "Price of the vehicles: $"
<< customVehicle1.GetPrice() + customVehicle2.GetPrice()
<< endl;
}
else if (input == 4)
{
Vehicle customVehicle1("Razor", "Scooter",
2019, 39, 950);
cout <<
customVehicle1.GetYearMakeModel();
}
else if (input == 5)
{
Vehicle muscleCar("Ford", "Mustang", 1968,
82550, 71000);
Vehicle electric("Toyota", "Prius", 2014,
27377, 12);
Vehicle suv("Mazda", "CX5", 2018, 28449,
11047);
vector<Vehicle> vehicles;
// TODO: Add the three Vehicle objects to the
vector using the push_back() function
// TODO: Print out each Vehicle by looping
through the vector and calling the Display() function for each
Vehicle object
}
return 0;
}
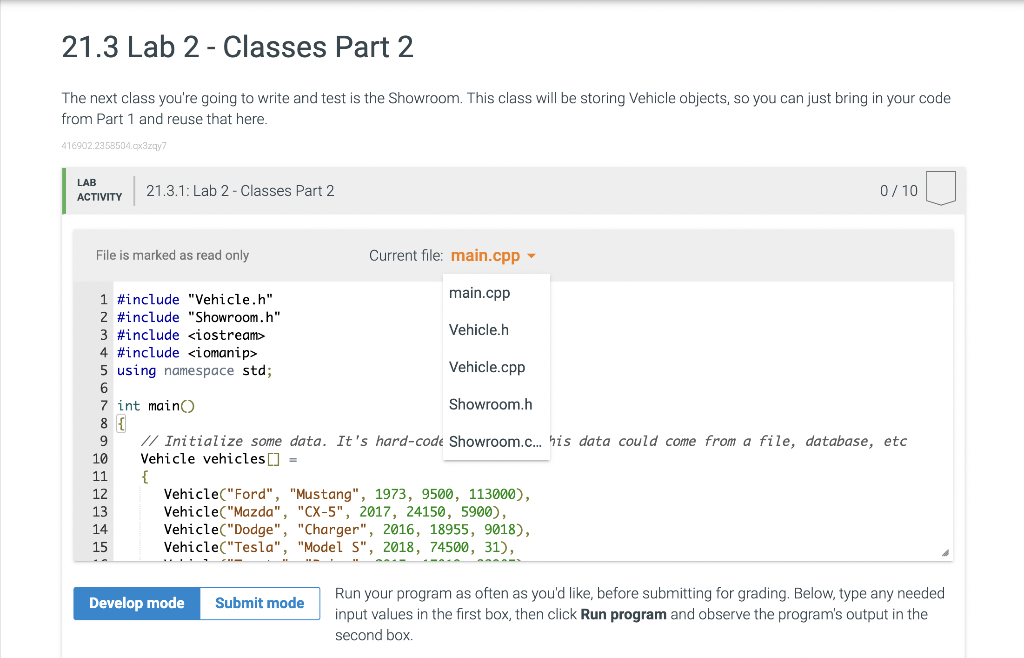
// Main.cpp code (does not modify)
#include "Vehicle.h"
#include "Showroom.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Initialize some data. It's hard-coded here,
but this data could come from a file, database, etc
Vehicle vehicles[] =
{
Vehicle("Ford", "Mustang",
1973, 9500, 113000),
Vehicle("Mazda", "CX-5",
2017, 24150, 5900),
Vehicle("Dodge", "Charger",
2016, 18955, 9018),
Vehicle("Tesla", "Model S",
2018, 74500, 31),
Vehicle("Toyota", "Prius",
2015, 17819, 22987),
Vehicle("Nissan", "Leaf",
2016, 12999, 16889),
Vehicle("Chevrolet", "Volt",
2015, 16994, 12558),
};
// Set the precision for showing prices with
2 decimal places
cout << std::fixed <<
std::setprecision(2);
int testNum;
cin >> testNum;
if (testNum == 1)
{
Showroom
testShowroom;
testShowroom.ShowInventory();
}
else if (testNum == 2)
{
Showroom one("Small Showroom", 2);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[5]);
one.ShowInventory();
}
else if (testNum == 3)
{
Showroom one("Full Showroom", 2);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[0]);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[5]);
one.ShowInventory();
}
else if (testNum == 4)
{
Showroom one("Price Test", 3);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[2]);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[4]);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[6]);
cout << "Total value: $"
<< one.GetInventoryValue();
}
else if (testNum == 5)
{
Showroom one("Room 1", 3);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[1]);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[5]);
cout << "Total value: $"
<< one.GetInventoryValue() << endl;
Showroom two("Room 2", 6);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[6]);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[5]);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[4]);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[2]);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[1]);
cout << "Total value: $" <<
two.GetInventoryValue();
}
return 0;
}
//main.cpp (code does not alter)
#include "Vehicle.h"
#include "Showroom.h"
#include "Dealership.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
void TestOne(Vehicle vehicles[]);
void TestTwo(Vehicle vehicles[]);
void TestThree(Vehicle vehicles[]);
void TestFour(Vehicle vehicles[]);
void TestFive(Vehicle vehicles[]);
void TestSix(Vehicle vehicles[]);
int main()
{
// Initialize some data. It's hard-coded here,
but this data could come from a file, database, etc
Vehicle vehicles[] =
{
Vehicle("Ford", "Mustang",
1973, 9500, 113000),
Vehicle("Mazda", "CX-5",
2017, 24150, 5900),
Vehicle("Dodge", "Charger",
2016, 18955, 9018),
Vehicle("Tesla", "Model S",
2018, 74500, 31),
Vehicle("Toyota", "Prius",
2015, 17819, 22987),
Vehicle("Nissan", "Leaf",
2016, 12999, 16889),
Vehicle("Chevrolet", "Volt",
2015, 16994, 12558),
};
// Set the precision for showing prices with
2 decimal places
cout << std::fixed <<
std::setprecision(2);
int testNum;
cin >> testNum;
if (testNum == 1)
TestOne(vehicles);
else if (testNum == 2)
TestTwo(vehicles);
else if (testNum == 3)
TestThree(vehicles);
else if (testNum == 4)
TestFour(vehicles);
else if (testNum == 5)
TestFive(vehicles);
else if (testNum == 6)
TestSix(vehicles);
return 0;
}
void TestOne(Vehicle vehicles[])
{
Dealership testDealership;
testDealership.ShowInventory();
}
void TestTwo(Vehicle vehicles[])
{
// Showrooms to store the vehicles
Showroom one("Test Room One", 3);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[2]);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[6]);
//showroom.AddVehicle(&vehicles[2]);
Showroom two("Test Room Two", 4);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[1]);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[2]);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
// A "parent" object to store the
Showrooms
Dealership dealership("COP3503 Vehicle
Emporium", 2);
dealership.AddShowroom(one);
dealership.AddShowroom(two);
dealership.ShowInventory();
}
void TestThree(Vehicle vehicles[])
{
// Showrooms to store the vehicles
Showroom one("Test Room One", 3);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[1]);
one.AddVehicle(vehicles[2]);
//showroom.AddVehicle(&vehicles[2]);
Showroom two("Test Room Two", 4);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[4]);
two.AddVehicle(vehicles[0]);
// A "parent" object to store the
Showrooms
Dealership dealership("COP3503 Vehicle
Emporium", 2);
dealership.AddShowroom(one);
dealership.AddShowroom(two);
// Should get an error message here
dealership.AddShowroom(two);
dealership.ShowInventory();
}
void TestFour(Vehicle vehicles[])
{
// Showrooms to store the
vehicles
Showroom showroom("Primary Showroom", 3);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[0]);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[1]);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[6]);
Showroom secondary("Fuel-Efficient Showroom", 4);
secondary.AddVehicle(vehicles[4]);
secondary.AddVehicle(vehicles[5]);
Showroom third("Fuel-Efficient Showroom",
4);
third.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
third.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
third.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
// A "parent" object to store the
Showrooms
Dealership dealership("COP3503 Vehicle
Emporium", 3);
dealership.AddShowroom(showroom);
dealership.AddShowroom(secondary);
dealership.AddShowroom(third);
cout << "Average price of the cars in
the dealership: $" << dealership.GetAveragePrice();
}
void TestFive(Vehicle vehicles[])
{
// Showrooms to store the
vehicles
Showroom showroom("Primary Showroom", 6);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[0]);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[1]);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[2]);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[4]);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[5]);
Showroom secondary("Fuel-Efficient Showroom", 4);
secondary.AddVehicle(vehicles[4]);
secondary.AddVehicle(vehicles[5]);
secondary.AddVehicle(vehicles[5]);
Showroom third("Fuel-Efficient Showroom",
4);
third.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
third.AddVehicle(vehicles[4]);
third.AddVehicle(vehicles[5]);
third.AddVehicle(vehicles[6]);
// A "parent" object to store the
Showrooms
Dealership dealership("COP3503 Vehicle
Emporium", 3);
dealership.AddShowroom(showroom);
dealership.AddShowroom(secondary);
dealership.AddShowroom(third);
cout << "Average price of the cars in
the dealership: $" << dealership.GetAveragePrice();
}
void TestSix(Vehicle vehicles[])
{
// Showrooms to store the
vehicles
Showroom showroom("Primary Showroom", 4);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[2]);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[4]);
showroom.AddVehicle(vehicles[6]);
Showroom third("Fuel-Efficient Showroom",
4);
third.AddVehicle(vehicles[3]);
third.AddVehicle(vehicles[5]);
third.AddVehicle(vehicles[6]);
// A "parent" object to store the
Showrooms
Dealership dealership("COP3503 Vehicle
Emporium", 3);
dealership.AddShowroom(showroom);
dealership.AddShowroom(third);
cout << "Average price of the cars in
the dealership: $" << dealership.GetAveragePrice();
}
Expert Answer
Answer For your requirements i have provided the indetail note:- as per chegg rules and regulations i have answered the question.(minimum no.of question this is the answer for ur question Step by step :- Vehicle.h #include #include