Home /
Expert Answers /
Mechanical Engineering /
the-permeability-coefficient-of-a-type-of-small-gas-molecule-in-a-polymer-is-dependent-on-absolute-pa196
(Solved): The permeability coefficient of a type of small gas molecule in a polymer is dependent on absolute ...
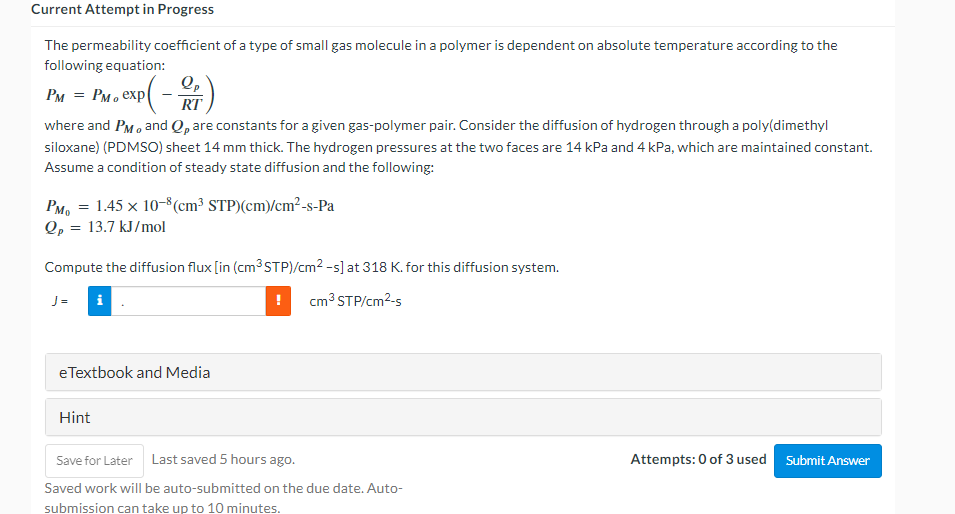
The permeability coefficient of a type of small gas molecule in a polymer is dependent on absolute temperature according to the following equation: \[ P_{M}=P_{M_{o}} \exp \left(-\frac{Q_{p}}{R T}\right) \] where and \( P_{M o} \) and \( Q_{p} \) are constants for a given gas-polymer pair. Consider the diffusion of hydrogen through a poly(dimethyl siloxane) (PDMSO) sheet \( 14 \mathrm{~mm} \) thick. The hydrogen pressures at the two faces are \( 14 \mathrm{kPa} \) and \( 4 \mathrm{kPa} \), which are maintained constant. Assume a condition of steady state diffusion and the following: \[ \begin{array}{l} P_{M_{0}}=1.45 \times 10^{-8}\left(\mathrm{~cm}^{3} \mathrm{STP}\right)(\mathrm{cm}) / \mathrm{cm}^{2}-\mathrm{s}-\mathrm{Pa} \\ Q_{p}=13.7 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol} \end{array} \] Compute the diffusion flux [in \( \left.\left(\mathrm{cm}^{3} \mathrm{STP}\right) / \mathrm{cm}^{2}-\mathrm{s}\right] \) at \( 318 \mathrm{~K} \). for this diffusion system. \[ J=\mid \quad \mathrm{cm}^{3} \mathrm{STP} / \mathrm{cm}^{2}-\mathrm{s} \] eTextbook and Media Hint Last saved 5 hours ago. Attempts: 0 of 3 used Saved work will be auto-submitted on the due date. Auto- submission can take un to 10 minutes.