Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemistry /
the-michael-reaction-is-a-conjugate-addition-process-wherein-a-nucleophilic-enolate-anion-the-don-pa495
(Solved): The Michael reaction is a conjugate addition process wherein a nucleophilic enolate anion (the don ...
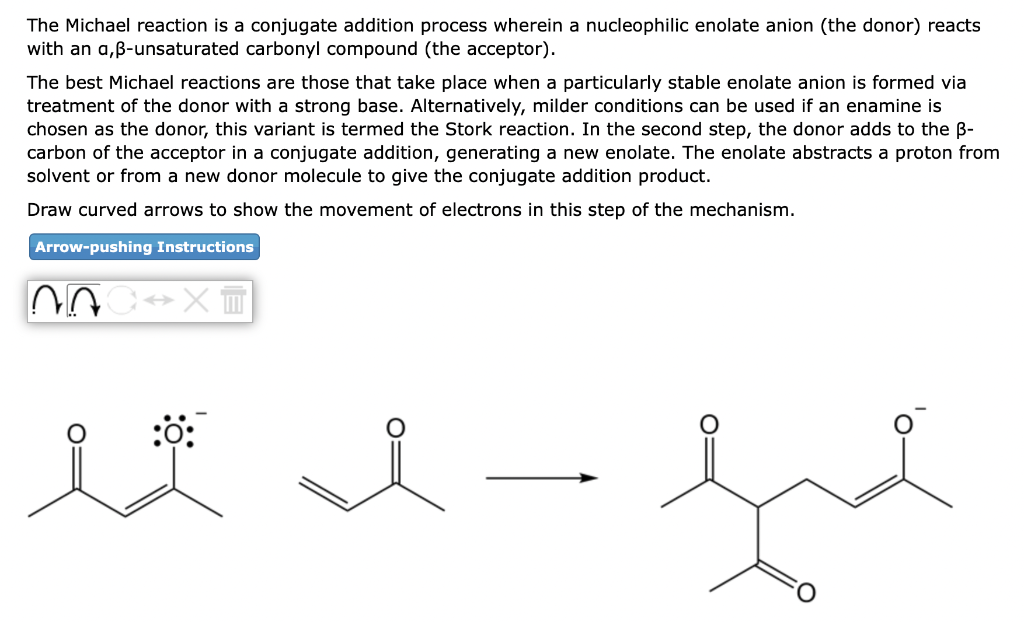
The Michael reaction is a conjugate addition process wherein a nucleophilic enolate anion (the donor) reacts with an a, \( \beta \)-unsaturated carbonyl compound (the acceptor). The best Michael reactions are those that take place when a particularly stable enolate anion is formed via treatment of the donor with a strong base. Alternatively, milder conditions can be used if an enamine is chosen as the donor, this variant is termed the Stork reaction. In the second step, the donor adds to the \( \beta \) carbon of the acceptor in a conjugate addition, generating a new enolate. The enolate abstracts a proton from solvent or from a new donor molecule to give the conjugate addition product. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism.
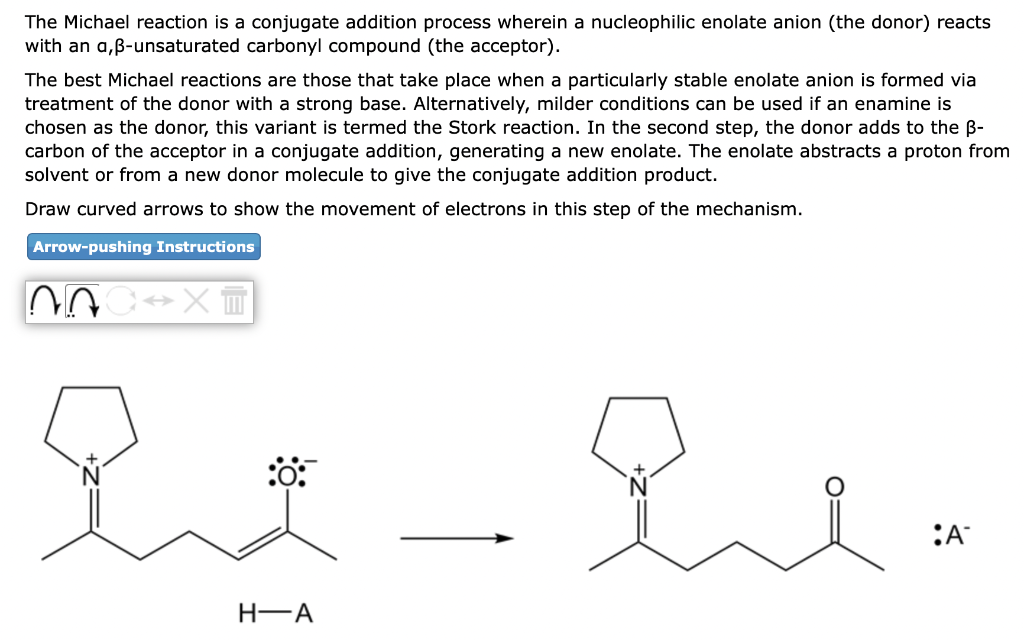
The Michael reaction is a conjugate addition process wherein a nucleophilic enolate anion (the donor) reacts with an a, \( \beta \)-unsaturated carbonyl compound (the acceptor). The best Michael reactions are those that take place when a particularly stable enolate anion is formed via treatment of the donor with a strong base. Alternatively, milder conditions can be used if an enamine is chosen as the donor, this variant is termed the Stork reaction. In the second step, the donor adds to the \( \beta \) carbon of the acceptor in a conjugate addition, generating a new enolate. The enolate abstracts a proton from solvent or from a new donor molecule to give the conjugate addition product. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. \( \longrightarrow \)