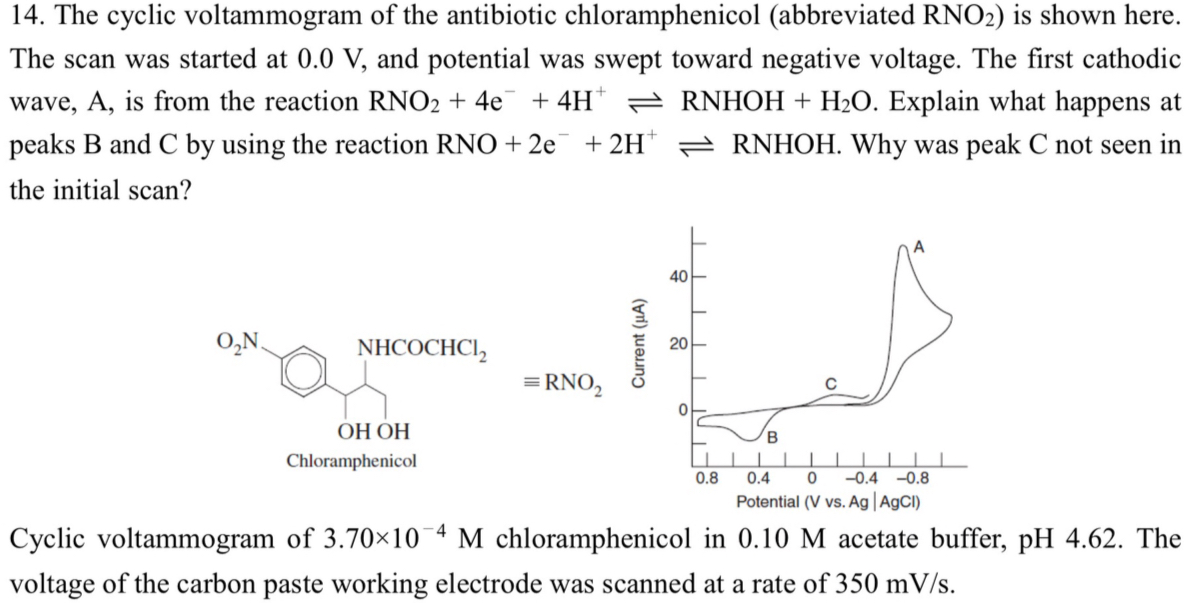
(Solved): The cyclic voltammogram of the antibiotic chloramphenicol (abbreviated RNO_(2) ) is shown here. The ...
Severity: Warning
Message: fopen(/home/answnniz/solutionspile.com/system/sessions/ci_sessiona59b3c515c517e85d5599a662f847212309fb63d): failed to open stream: Disk quota exceeded
Filename: drivers/Session_files_driver.php
Line Number: 176
Backtrace:
File: /home/answnniz/solutionspile.com/index.php
Line: 367
Function: require_once
Severity: Warning
Message: session_start(): Failed to read session data: user (path: /home/answnniz/solutionspile.com/system/sessions)
Filename: Session/Session.php
Line Number: 143
Backtrace:
File: /home/answnniz/solutionspile.com/index.php
Line: 367
Function: require_once
