Home /
Expert Answers /
Statistics and Probability /
state-h0-and-ha-in-words-and-in-symbols-then-determine-whether-the-hypothesis-test-is-left-t-pa267
(Solved): State H0 and Ha in words and in symbols. Then determine whether the hypothesis test is left-t ...
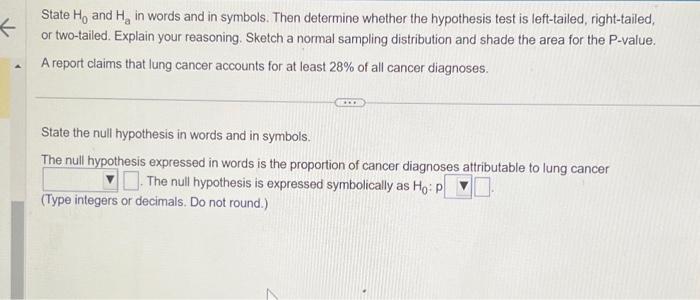
State and in words and in symbols. Then determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed. Explain your reasoning. Sketch a normal sampling distribution and shade the area for the -value. A report claims that lung cancer accounts for at least of all cancer diagnoses. State the null hypothesis in words and in symbols. The null hypothesis expressed in words is the proportion of cancer diagnoses attributable to lung cancer The null hypothesis is expressed symbolically as (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.)
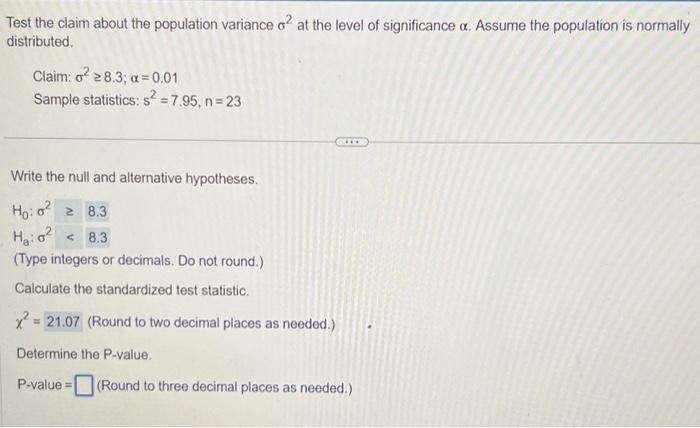
Test the claim about the population variance at the level of significance . Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: Sample statistics: Write the null and alternative hypotheses. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) Calculate the standardized test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. P-value (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
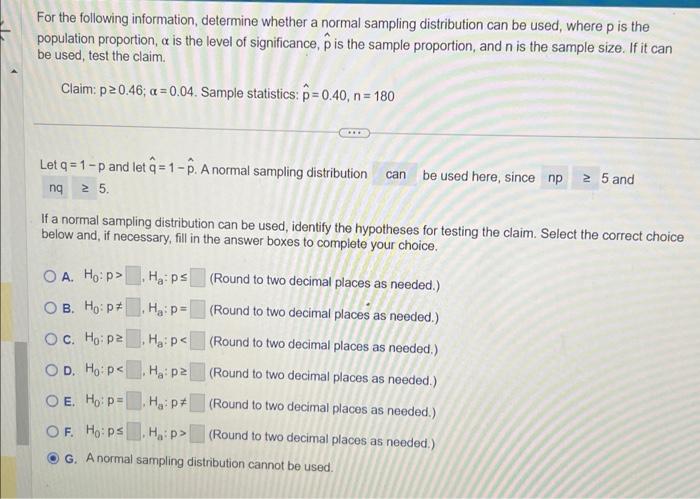
For the following information, determine whether a normal sampling distribution can be used, where is the population proportion, is the level of significance, is the sample proportion, and is the sample size. If it can be used, test the claim. Claim: . Sample statistics: Let and let . A normal sampling distribution be used here, since 5 and . If a normal sampling distribution can be used, identify the hypotheses for testing the claim. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. A. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) B. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) C. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) D. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) E. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) F. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) G. A normal sampling distribution cannot be used.