Home /
Expert Answers /
Biology /
read-the-following-figure-6-and-provide-a-summary-of-what-the-figure-tells-shows-us-and-how-it-regar-pa173
(Solved): Read the following figure 6 and provide a summary of what the figure tells/shows us AND how it regar ...
Read the following figure 6 and provide a summary of what the figure tells/shows us AND how it regards to this study:
Article title: Staphylococcus aureus Uses the GraXRS Regulatory System To Sense and Adapt to the Acidified Phagolysosome in Macrophages
A B S T R A C T: Macrophages are critical to innate immunity due to their ability to phagocytose bacteria. The macrophage phagolysosome is a highly acidic organelle with potent antimicrobial properties, yet remarkably, ingested Staphylococcus aureus replicates within this niche. Herein we demonstrate that S. aureus requires the GraXRS regulatory system for growth within this niche, while the SaeRS and AgrAC two-component regulatory systems and the -phenol soluble modulins are dispens- able. Importantly, we find that it is exposure to acidic pH that is required for optimal growth of S. aureus inside fully acidified macrophage phagolysosomes. Exposure of S. aureus to acidic pH evokes GraS signaling, which in turn elicits an adaptive re- sponse that endows the bacteria with increased resistance to antimicrobial effectors, such as antimicrobial peptides, encountered inside macrophage phagolysosomes. Notably, pH-dependent induction of antimicrobial peptide resistance in S. aureus re- quires the GraS sensor kinase. GraS and MprF, a member of the GraS regulon, play an important role for bacterial survival in the acute stages of systemic infection, where in murine models of infection, S. aureus resides within liver-resident Kupffer cells. We conclude that GraXRS represents a vital regulatory system that functions to allow S. aureus to evade killing, prior to commencement of replication, within host antibacterial immune cells.
Please explain in detail figures A-C. Thank you. Will give like!

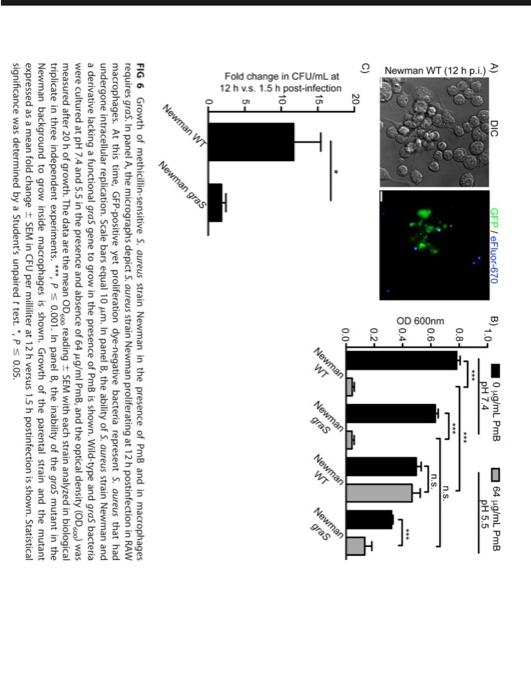
Flannagan et al. FIG 6 Growth of methicillin-sensitive S. aureus strain Newman in the presence of PmB and in macrophages requires graS, In panel A, the micrographs depict S. aureus strain Newman proliferating at postinfection in RAW macrophages. At this time, GFP-positive yet proliferation dye-negative bacteria represent . oureus that had undergone intracellular replication. Scale bars equal , In panel B, the ability of S. aureus strain Newman and a derivative lacking a functional gras gene to grow in the presence of is shown. Wild-type and gras bacteria were cultured at and 5.5 in the presence and absence of , and the optical density was measured after of growth. The data are the mean reading with each strain analyzed in biological triplicate in three independent experiments. , In panel , the inability of the gras mutant in the Newman background to grow inside macrophages is shown. Growth of the parental strain and the mutant expressed as a mean fold change in CFU per milliliter at versus postinfection is shown. Statistical significance was determined by a Student's unpaired test. ", .
FIG 6 Growth of methicillin-sensitive S, dureus strain Newman in the presence of PmB and in macrophages requires graS. In panel A, the micrographs depict S. aureus strain Newman proliferating at postinfection in RAW macrophages. At this time, GFP-positive yet proliferation dye-negative bacteria represent . aureus that had undergone intracellular replication. Scale bars equal . In panel B, the ability of S, aureus strain Newman and a derivative lacking a functional gras gene to grow in the presence of is shown. Wild-type and gras bacteria were cultured at and 5.5 in the presence and absence of , and the optical density ) was measured after of growth. The data are the mean reading \pm SEM with each strain analyzed in biological triplicate in three independent experiments. . In panel , the inability of the gras mutant in the Newman background to grow inside macrophages is shown. Growth of the parental strain and the mutant expressed as a mean fold change in CFU per milliliter at versus postinfection is shown. Statistical significance was determined by a Student's unpaired test.,.