Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemistry /
question-4-figure-1-describes-an-electrochemical-cell-divided-by-an-ideal-cation-exchange-membran-pa327
(Solved): QUESTION 4: Figure 1 describes an electrochemical cell divided by an ideal cation exchange membran ...
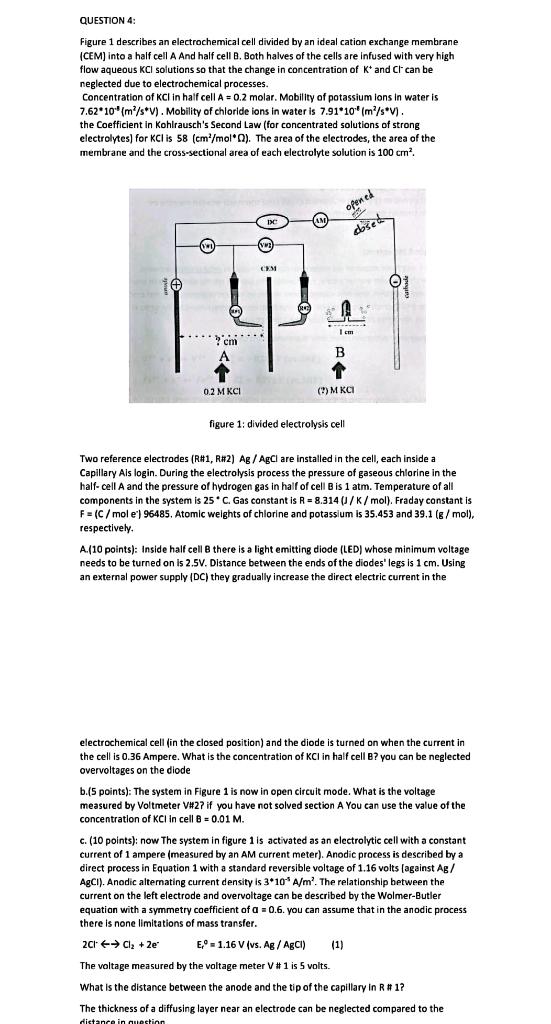
QUESTION 4: Figure 1 describes an electrochemical cell divided by an ideal cation exchange membrane (CEM) into a half cell A And half cell B. Both halves of the cells are infused with very high flow aqueous KCI solutions so that the change in concentration of K* and Ct can be neglected due to electrochemical processes. Concentration of KCI in half cell A = 0.2 molar. Mobility of potassium ions in water is 7.62*10 (m²/s*V). Mobility of chloride ions in water is 7.91*10* (m²/s V). the Coefficient in Kohlrausch's Second Law (for concentrated solutions of strong electrolytes) for KCI is 58 (cm²/mol ). The area of the electrodes, the area of the membrane and the cross-sectional area of each electrolyte solution is 100 cm². 7 cm - K 0.2 MKCI DC (VW) CEM GE opened dosed Av Icm B (2) MKCI figure 1: divided electrolysis cell Two reference electrodes (R#1, R#2) Ag/AgCl are installed in the cell, each inside a Capillary Ais login. During the electrolysis process the pressure of gaseous chlorine in the half-cell A and the pressure of hydrogen gas in half of cell B is 1 atm. Temperature of all components in the system is 25° C. Gas constant is R = 8.314 (J/K/mol). Fraday constant is F = (C/mol e) 96485. Atomic weights of chlorine and potassium is 35.453 and 39.1 (g/mol), respectively. A.(10 points): Inside half cell B there is a light emitting diode (LED) whose minimum voltage needs to be turned on is 2.5V. Distance between the ends of the diodes' legs is 1 cm. Using an external power supply (DC) they gradually increase the direct electric current in the electrochemical cell (in the closed position) and the diode is turned on when the current in the cell is 0.36 Ampere. What is the concentration of KCI in half cell B? you can be neglected overvoltages on the diode. b.(5 points): The system in Figure 1 is now in open circuit mode. What is the voltage measured by Voltmeter V#2? if you have not solved section A You can use the value of the concentration of KCI in cell B = 0.01 M. c. (10 points): now The system in figure 1 is activated as an electrolytic cell with a constant current of 1 ampere (measured by an AM current meter). Anodic process is described by a direct process in Equation 1 with a standard reversible voltage of 1.16 volts (against Ag/ AgCl). Anodic alternating current density is 3*10 A/m². The relationship between the current on the left electrode and overvoltage can be described by the Wolmer-Butler equation with a symmetry coefficient of a = 0.6. you can assume that in the anodic process there is none limitations of mass transfer. (1) 2Cl ?? Cl? +2e² E, 1.16 V (vs. Ag / AgCl) The voltage measured by the voltage meter V # 1 is 5 volts. What is the distance between the anode and the tip of the capillary in R # 1? The thickness of a diffusing layer near an electrode can be neglected compared to the distance in question