Home /
Expert Answers /
Accounting /
problem-6-2a-calculate-ending-inventory-cost-of-goods-sold-sales-revenue-and-gross-profit-for-fo-pa395
(Solved): Problem 6-2A Calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit for fo ...
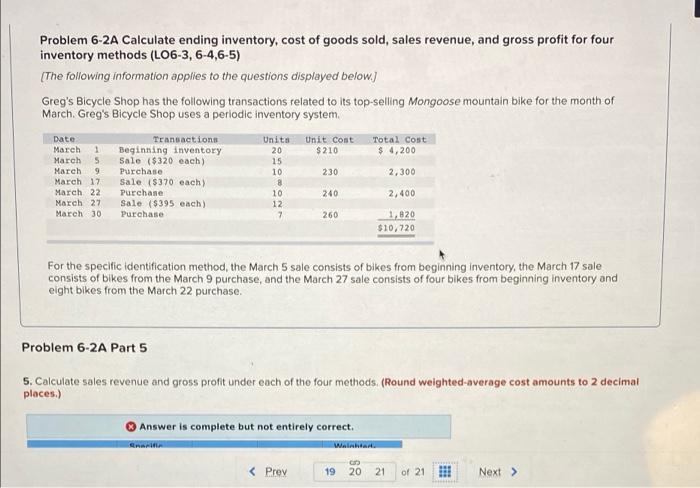
Problem 6-2A Calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit for four inventory methods (LO6-3, 6-4,6-5) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Greg's Bicycle Shop has the following transactions related to its top-selling Mongoose mountain bike for the month of March. Greg's Bicycle Shop uses a periodic inventory system. Date Transactions Unita Unit Cost $210 March 1 Beginning inventory Total Cost $4,200 20 March 5 Sale ($320 each) 15 March 9 Purchase 10 230 2,300 March 17. Sale ($370 each) 8 Purchase 10 240 2,400 March 22 March 27 March 30, 12 Sale ($395 each) Purchase 7 260 1,820 $10,720 For the specific identification method, the March 5 sale consists of bikes from beginning inventory, the March 17 sale consists of bikes from the March 9 purchase, and the March 27 sale consists of four bikes from beginning inventory and eight bikes from the March 22 purchase. Problem 6-2A Part 5 5. Calculate sales revenue and gross profit under each of the four methods. (Round weighted-average cost amounts to 2 decimal places.) Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Wainhted. < Prev of 21 Next > 19 S 20 21
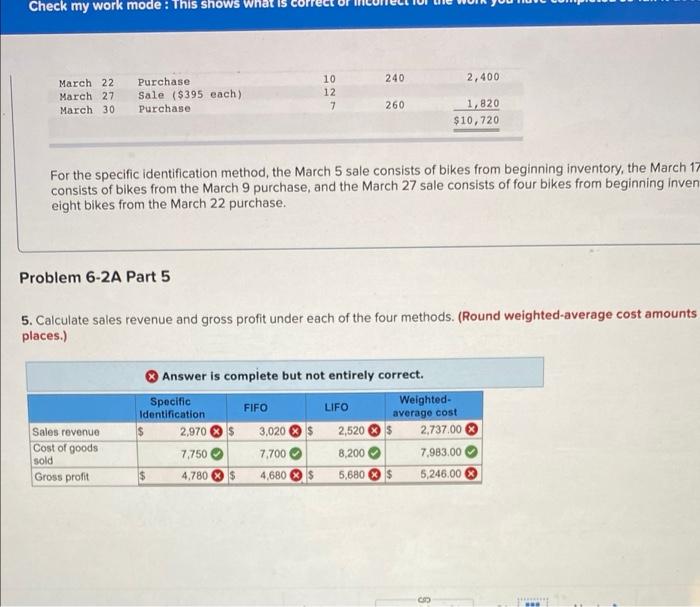
Check my work mode: This shows what is March 22 Purchase 10 240 2,400 12 March 27 Sale ($395 each) Purchase March 30 7 260 1,820 $10,720 For the specific identification method, the March 5 sale consists of bikes from beginning inventory, the March 17 consists of bikes from the March 9 purchase, and the March 27 sale consists of four bikes from beginning inven eight bikes from the March 22 purchase. Problem 6-2A Part 5 5. Calculate sales revenue and gross profit under each of the four methods. (Round weighted-average cost amounts places.) Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Specific FIFO LIFO Identification Sales revenue 2,970 $ Cost of goods sold 7,750 Gross profit $ 4,780 $ 3,020 $ 7,700 4,680 $ 2,520 8,200 5,680 Weighted- average cost 2,737.00 7,983.00 5,246.00 $ $ ********* www