Home /
Expert Answers /
Electrical Engineering /
principles-of-dc-machines-9-of-11-learning-goal-use-the-principles-of-dc-machines-to-design-and-a-pa441
(Solved): Principles of DC Machines 9 of 11 Learning Goal: Use the principles of dc machines to design and a ...
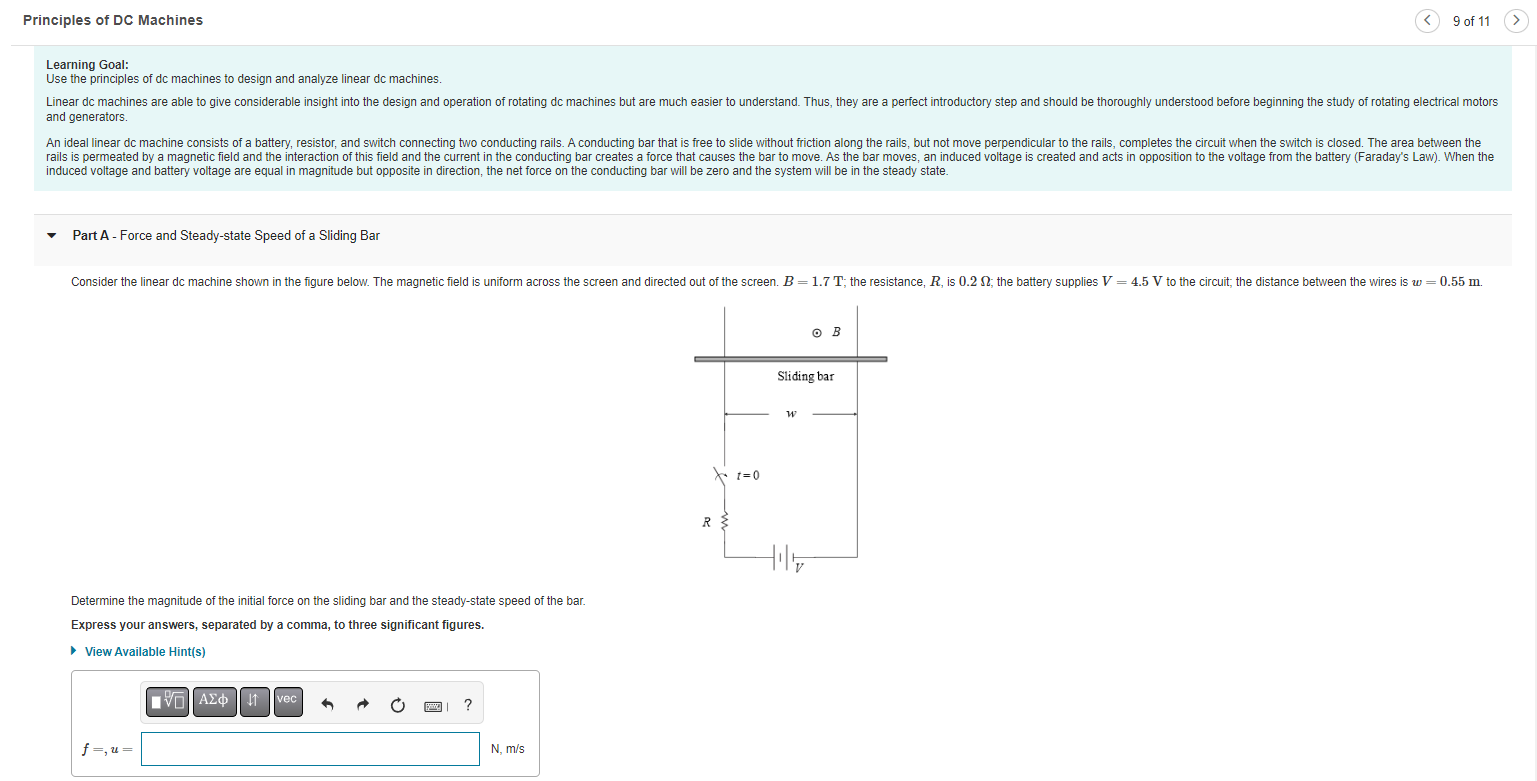
Principles of DC Machines 9 of 11 Learning Goal: Use the principles of dc machines to design and analyze linear dc machines. Linear dc machines are able to give considerable insight into the design and operation of rotating dc machines but are much easier to understand. Thus, they are a perfect introductory step and should be thoroughly understood before beginning the study of rotating electrical motors and generators. An ideal linear dc machine consists of a battery, resistor, and switch connecting two conducting rails. A conducting bar that is free to slide without friction along the rails, but not move perpendicular to the rails, completes the circuit when the switch is closed. The area between the rails is permeated by a magnetic field and the interaction of this field and the current in the conducting bar creates a force that causes the bar to move. As the bar moves, an induced voltage is created and acts in opposition to the voltage from the battery (Faraday's Law). When the induced voltage and battery voltage are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, the net force on the conducting bar will be zero and the system will be in the steady state. Part A - Force and Steady-state Speed of a Sliding Bar Consider the linear dc machine shown in the figure below. The magnetic field is uniform across the screen and directed out of the screen. B = 1.7 T; the resistance, R, is 0.2 S2; the battery supplies V 4.5 V to the circuit; the distance between the wires is w = 0.55 m. OB Determine the magnitude of the initial force on the sliding bar and the steady-state speed of the bar. Express your answers, separated by a comma, to three significant figures. ? View Available Hint(s) IVE | ??? 41 vec f=, u = N, m/s x+1=0 R { Sliding bar W t?lm
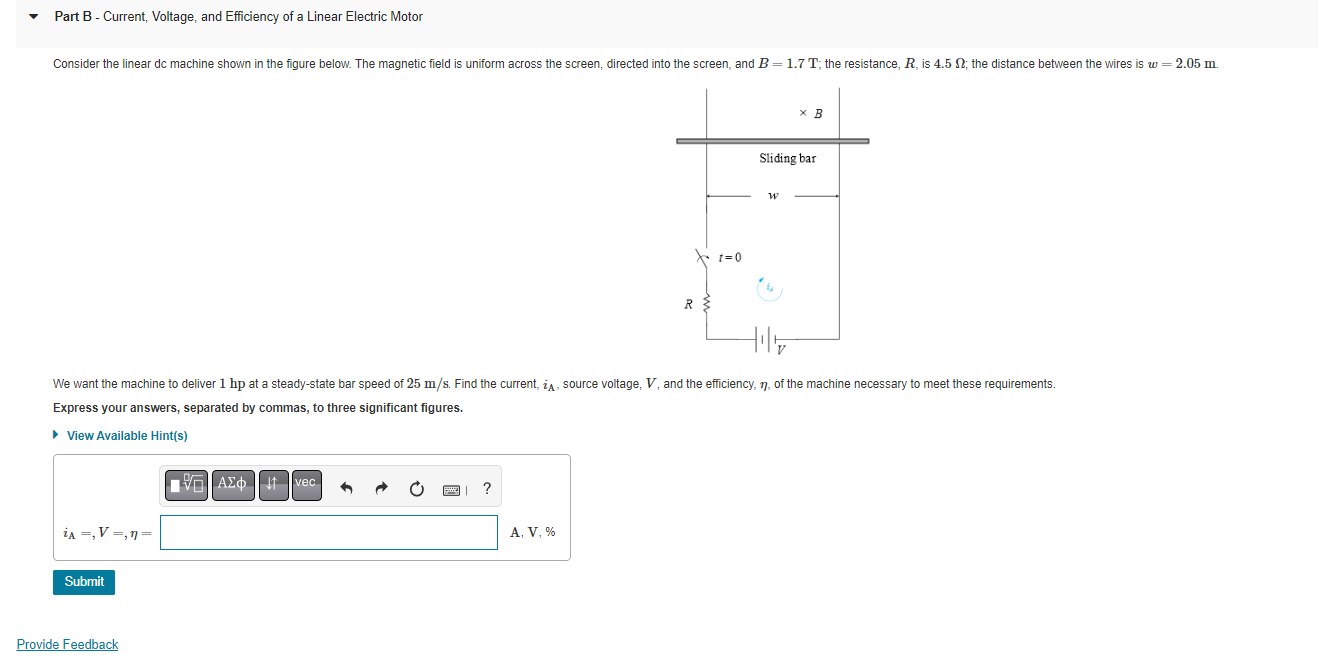
Part B - Current, Voltage, and Efficiency of a Linear Electric Motor Consider the linear dc machine shown in the figure below. The magnetic field is uniform across the screen, directed into the screen, and B = 1.7 T; the resistance, R, is 4.5 2; the distance between the wires is w = 2.05 m. B Sliding bar R We want the machine to deliver 1 hp at a steady-state bar speed of 25 m/s. Find the current, ¿A, source voltage, V, and the efficiency, 7, of the machine necessary to meet these requirements. Express your answers, separated by commas, to three significant figures. ? View Available Hint(s) ????? vec ? iA =, V =,n= A, V, % Submit Provide Feedback t=0
Expert Answer
Q1 . Solution : The force on the bar is given by F = B*I*L. ( equation-1) where B is magnetic field , I is current and L is length of bar. Clearly L = w = 0.55 m I = V/R =