Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemical Engineering /
p-and-q-are-isomers-of-dicarboxylic-acid-mathrm-c-4-mathrm-h-4-mathrm-o-pa224
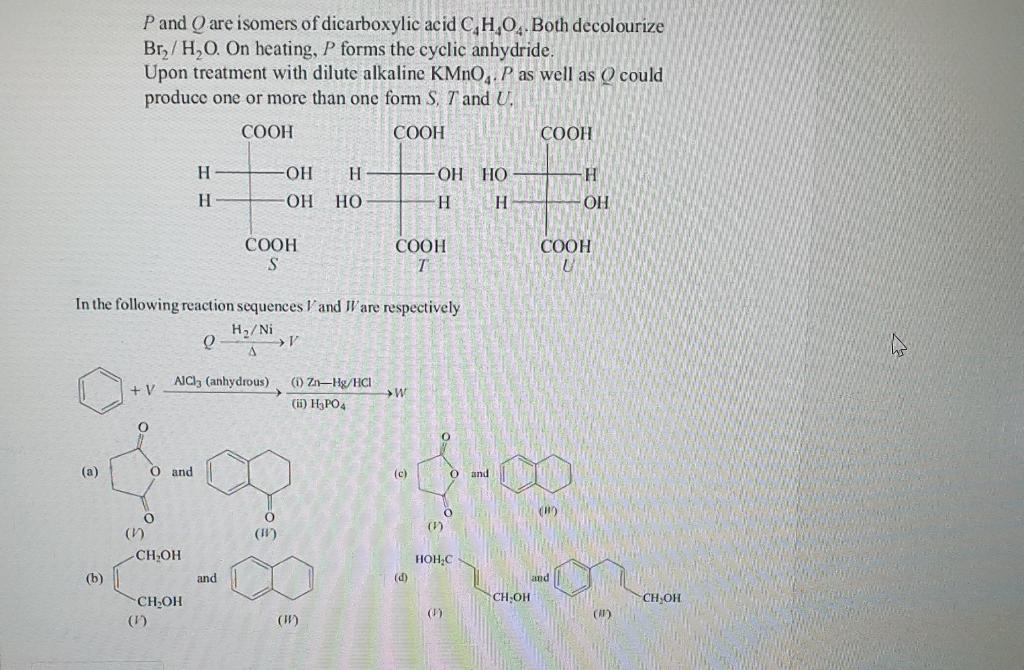
(Solved): \( P \) and \( Q \) are isomers of dicarboxylic acid \( \mathrm{C}_{4} \mathrm{H}_{4} \mathrm{O}_{ ...
\( P \) and \( Q \) are isomers of dicarboxylic acid \( \mathrm{C}_{4} \mathrm{H}_{4} \mathrm{O}_{4} \). Both decolourize \( \mathrm{Br}_{2} / \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \). On heating, \( P \) forms the cyclic anhydride. Upon treatment with dilute alkaline \( \mathrm{KMnO}_{4} \cdot P \) as well as \( Q \) could produce one or more than one form \( S, T \) and \( U \). In the following reaction sequences \( \mathrm{V} \) and \( \mathrm{J} \) are respectively \[ Q \stackrel{\mathrm{H}_{2} / \mathrm{Ni}}{\Delta} \mathrm{V} \] (a) (c) (b) (ii) (ii) (b) (b) and (d) (I) (ii) (?) (ii)