Home /
Expert Answers /
Economics /
nbsp-price-discrimination-and-welfare-on-the-following-graph-use-the-black-point-plus-symbol-pa331
(Solved): Price discrimination and welfare On the following graph, use the black point (plus symbol ...
Price discrimination and welfare
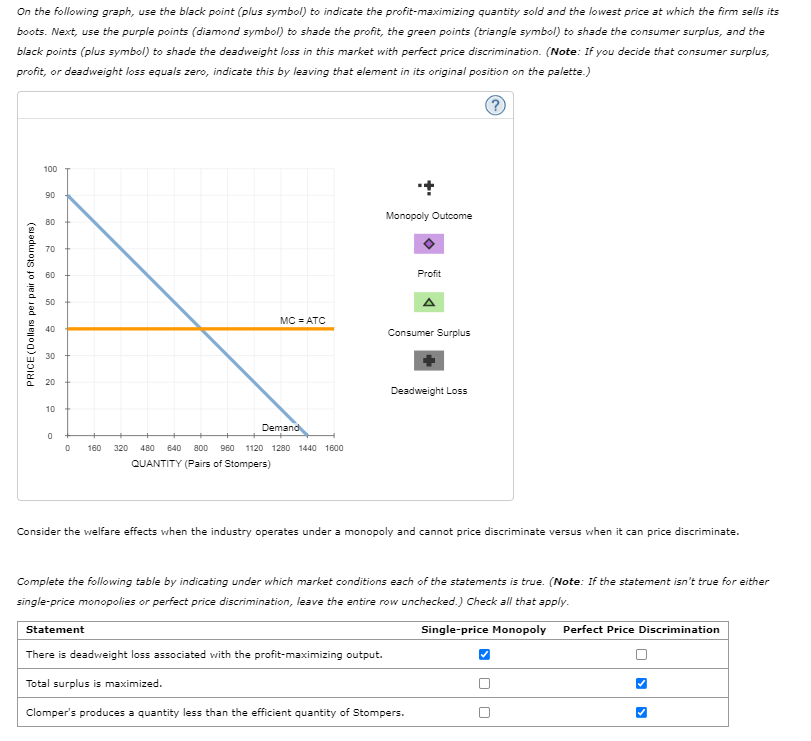
On the following graph, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing quantity sold and the lowest price at which the firm sells its boots. Next, use the purple points (diamond symbol) to shade the profit, the green points (triangle symbol) to shade the consumer surplus, and the black points (plus symbol) to shade the deadweight loss in this market with perfect price discrimination. (Note: If you decide that consumer surplus, profit, or deadweight loss equals zero, indicate this by leaving that element in its original position on the palette.) Consider the welfare effects when the industry operates under a monopoly and cannot price discriminate versus when it can price discriminate. Complete the following table by indicating under which market conditions each of the statements is true. (Note: If the statement isn't true for either single-price monopolies or perfect price discrimination, leave the entire row unchecked.) Check all that apply.
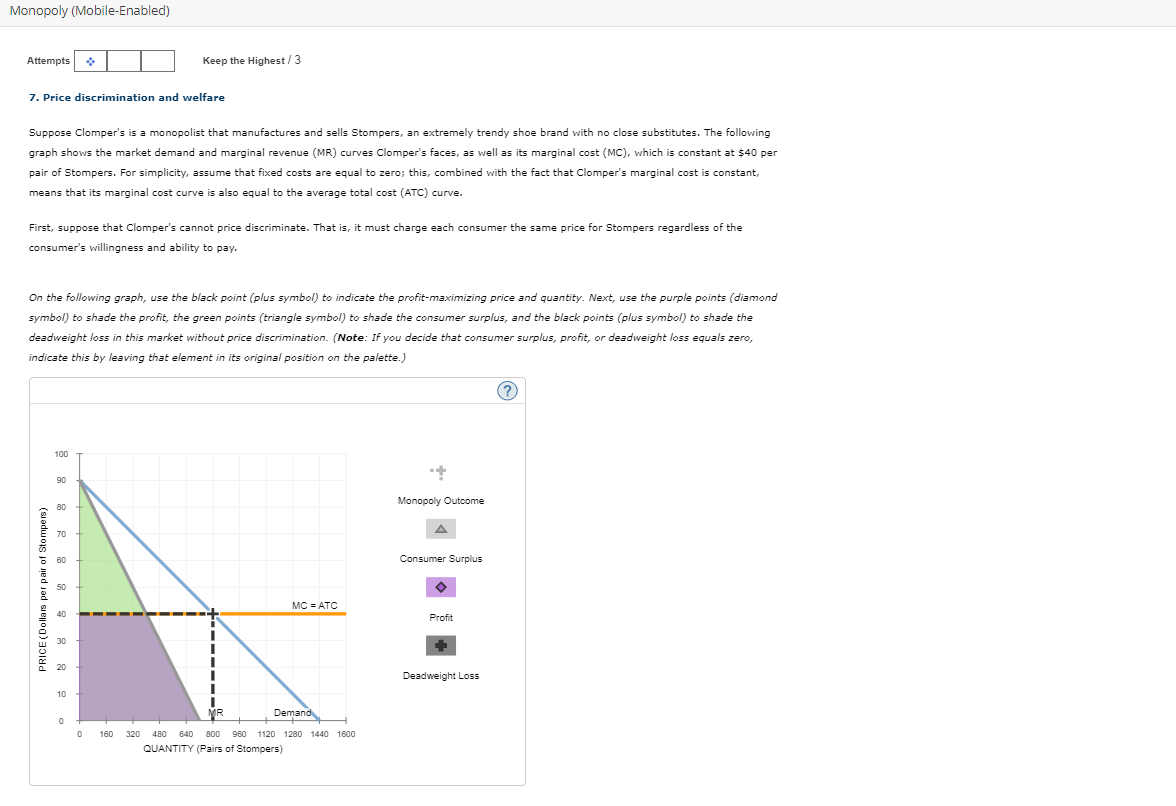
7. Price discrimination and welfare Suppose Clomper's is a monopolist that manufactures and sells Stompers, an extremely trendy shoe brand with no close substitutes. The following graph shows the market demand and marginal revenue (MR) curves Clomper's faces, as well as its marginal cost (MC), which is constant at \( \$ 40 \) per pair of Stompers. For simplicity, assume that fixed costs are equal to zero; this, combined with the fact that Clomper's marginal cost is constant, means that its marginal cost curve is also equal to the average total cost (ATC) curve. First, suppose that Clomper's cannot price discriminate. That is, it must charge each consumer the same price for Stompers regardless of the consumer's willingness and ability to pay. On the following graph, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity. Next, use the purple points (diamond symbol) to shade the profit, the green points (triangle symbol) to shade the consumer surplus, and the black points (plus symbol) to shade the deadweight loss in this market without price discrimination. (Note: If you decide that consumer surplus, profit, or deadweight loss equals zero, indicate this by leaving that element in its original position on the palette.)
Expert Answer
Introduction Considering the information