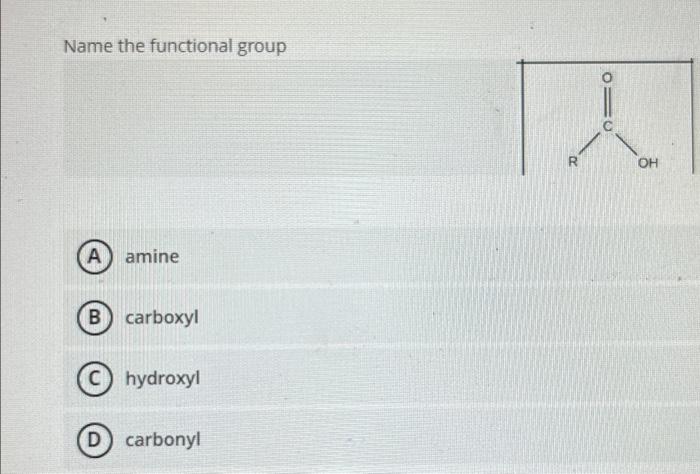
Expert Answer
A functional group is a specific group of atoms or bonds within a molecule that determines the molecule's chemical properties and reactivity. It is responsible for giving a compound its characteristic functional behavior. Functional groups are often involved in chemical reactions and can determine the type of reactions a compound can undergo.Some common functional groups include:Hydroxyl group (-OH): Found in alcohols, it imparts properties such as polarity and the ability to form hydrogen bonds.Carbonyl group (C=O): Present in aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids, it imparts properties like reactivity and polarity.Carboxyl group (-COOH): Found in carboxylic acids, it imparts acidity and participates in reactions such as esterification and amidation.Amino group (-NH2): Present in amines and amino acids, it imparts basicity and can participate in reactions such as protonation and condensation.Alkyl group (-R): Represents a hydrocarbon chain or part of it, such as methyl (-CH3), ethyl (-CH2CH3), or propyl (-CH2CH2CH3). Alkyl groups determine the structure and properties of many organic compounds.Ester group (-COO-): Found in esters, it imparts fruity smells and participates in reactions such as hydrolysis.Nitro group (-NO2): Present in nitro compounds, it imparts reactivity and can participate in reduction or substitution reactions.