Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemistry /
learning-goal-to-use-the-arrhenius-equation-to-calculate-the-activation-energy-as-temperature-ris-pa863
(Solved): Learning Goal: To use the Arrhenius equation to calculate the activation energy. As temperature ris ...


Learning Goal: To use the Arrhenius equation to calculate the activation energy. As temperature rises, the average kinetic energy of molecules increases. In a chemical reaction, this means that a higher percentage of the molecules possess the required activation energy, and the reaction goes faster. This relationship is shown by the Arrhenius equation where is the rate constant, is the frequency factor, is the activation energy, is the gas constant, and is the Kelvin temperature. The following rearranged version of the equation is also useful: where is the rate constant at temperature , and is the rate constant at temperature .
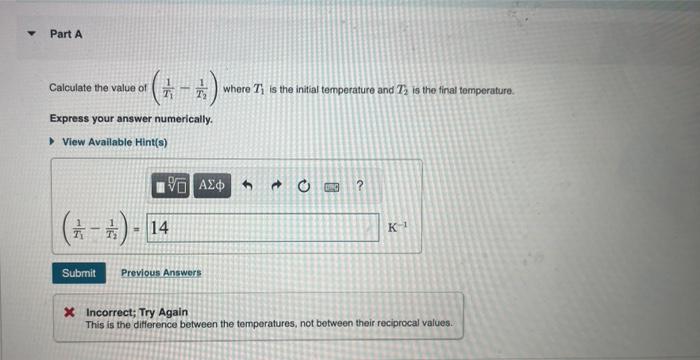
The rate constant of a chemical reaction increased from to upon raising the temperature from to .
Calculate the value of where is the initial temperature and is the final temperature. Express your answer numerically. Incorrect; Try Again This is the difference between the temperatures, not between their reciprocal values.
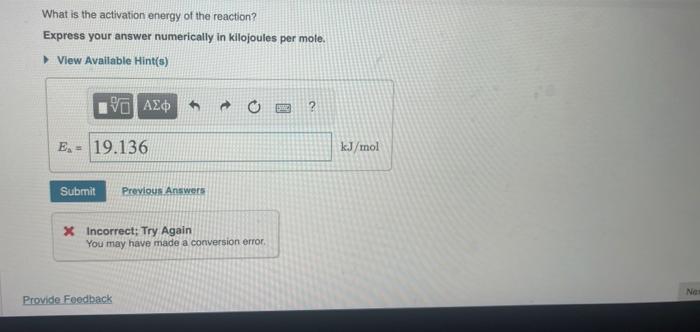
What is the activation energy of the reaction? Express your answer numerically in kilojoules per mole. * Incorrect; Try Again You may have made a conversion error.