Home /
Expert Answers /
Mechanical Engineering /
introduction-brief-description-of-the-structure-mechanism-a-riveter-is-a-tool-used-to-fasten-pa121
(Solved): Introduction: Brief description of the structure mechanism A riveter is a tool used to fasten ...
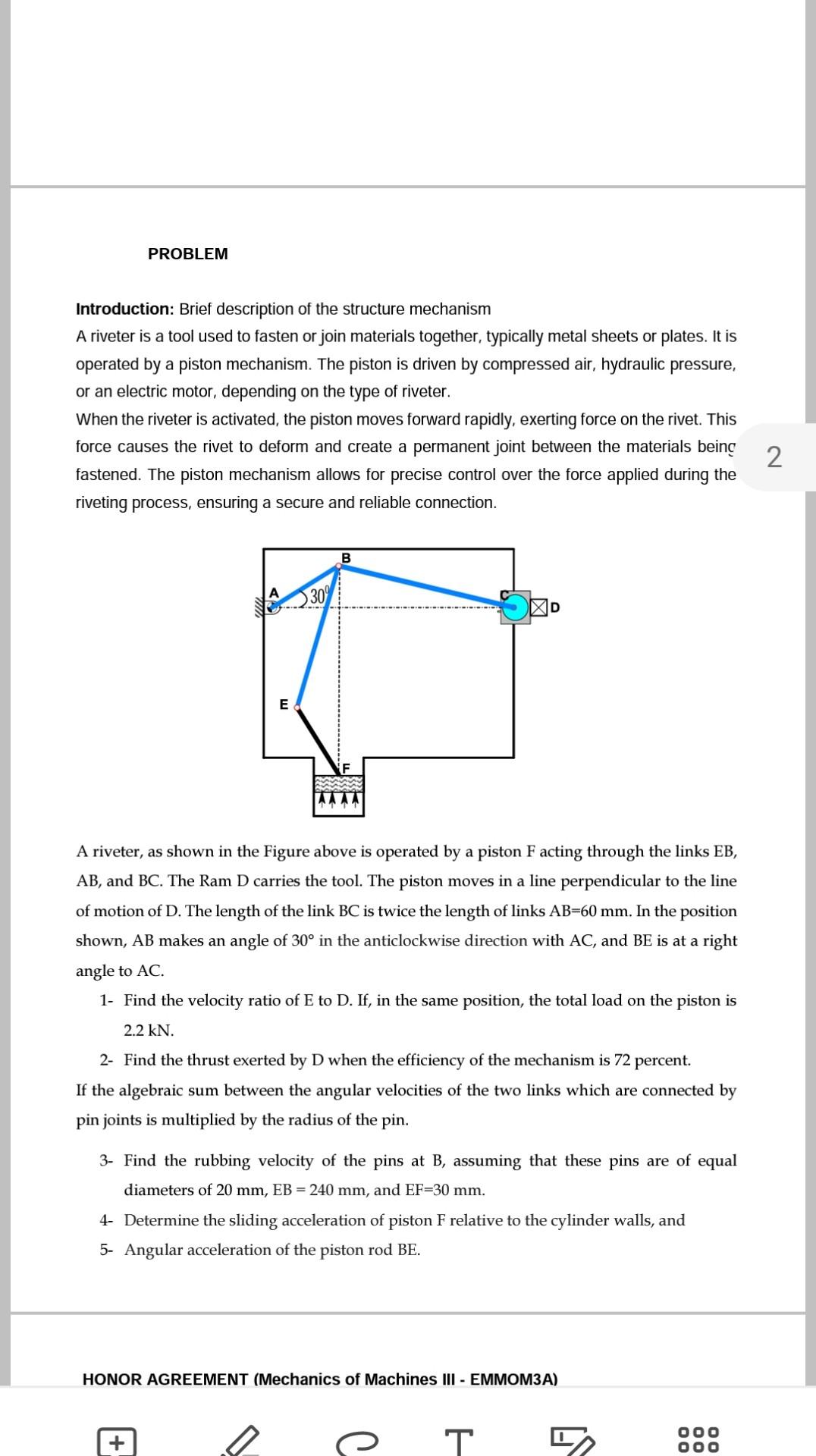
Introduction: Brief description of the structure mechanism A riveter is a tool used to fasten or join materials together, typically metal sheets or plates. It is operated by a piston mechanism. The piston is driven by compressed air, hydraulic pressure, or an electric motor, depending on the type of riveter. When the riveter is activated, the piston moves forward rapidly, exerting force on the rivet. This force causes the rivet to deform and create a permanent joint between the materials beinc fastened. The piston mechanism allows for precise control over the force applied during the riveting process, ensuring a secure and reliable connection. A riveter, as shown in the Figure above is operated by a piston F acting through the links EB, , and . The Ram D carries the tool. The piston moves in a line perpendicular to the line of motion of . The length of the link is twice the length of links . In the position shown, makes an angle of in the anticlockwise direction with , and is at a right angle to . 1- Find the velocity ratio of to . If, in the same position, the total load on the piston is . 2- Find the thrust exerted by D when the efficiency of the mechanism is 72 percent. If the algebraic sum between the angular velocities of the two links which are connected by pin joints is multiplied by the radius of the pin. 3- Find the rubbing velocity of the pins at , assuming that these pins are of equal diameters of , and . 4- Determine the sliding acceleration of piston relative to the cylinder walls, and 5- Angular acceleration of the piston rod . HONOR AGREEMENT (Mechanics of Machines III - EMMOM3A)
Expert Answer
Velocity ratio of E to D: The velocity ratio can b...