Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemistry /
if-an-external-stress-is-applied-to-a-reaction-at-equilibrium-the-reaction-responds-by-movin-pa127
(Solved): If an external stress is applied to a reaction at equilibrium, the reaction responds by movin ...
If an external “stress” is applied to a reaction at equilibrium, the reaction responds by moving in either the forward or reverse direction to reestablish the equilibrium defined by Kc.
Le Châtelier's principle states that if a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed by changing the conditions, the position of equilibrium shifts to counteract the change to reestablish an equilibrium.
Three external stresses that can disrupt equilibria are:
- Changing concentration
- Changing temperature
- Changing volume of reaction container
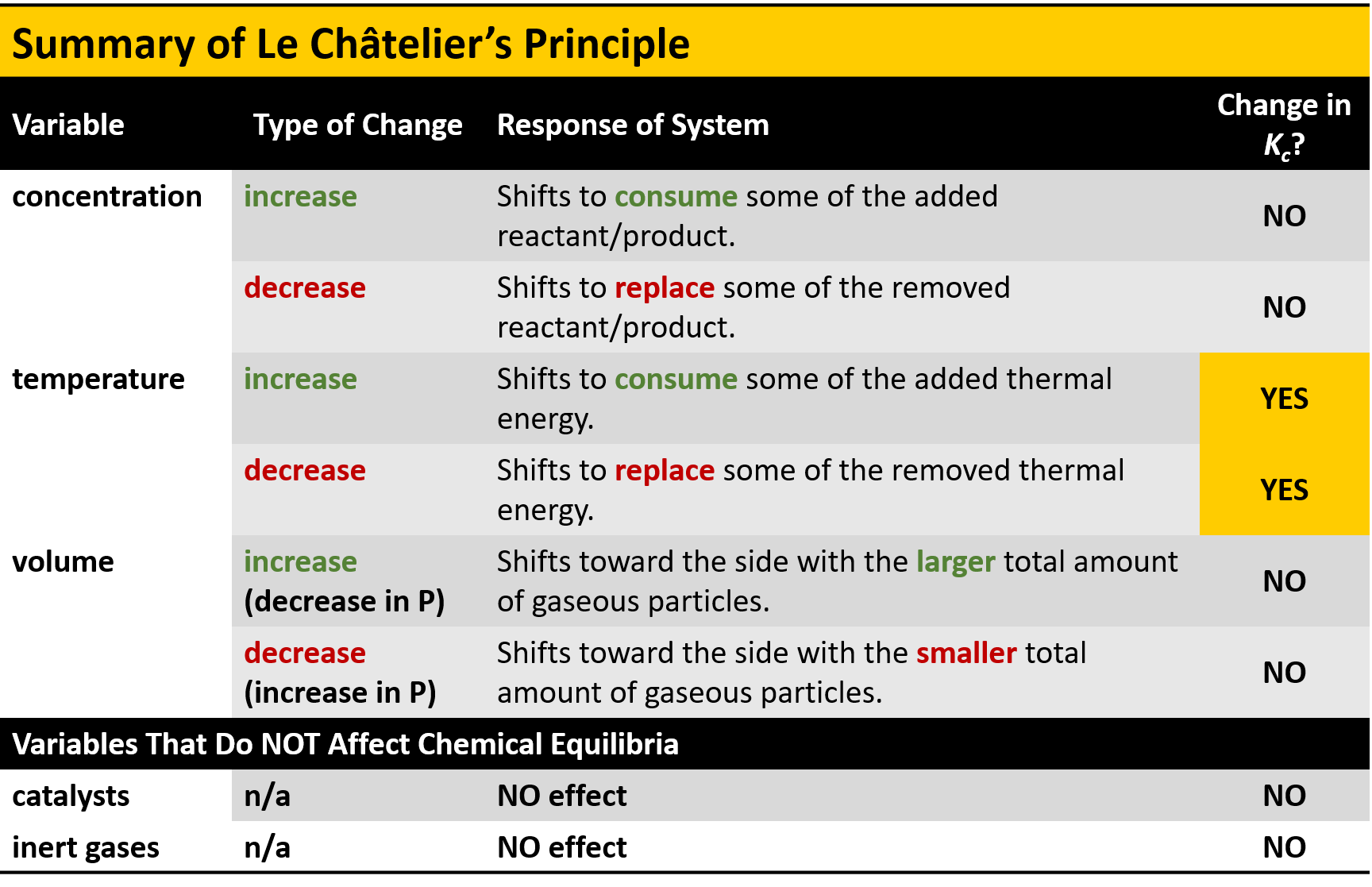
Summary of Le Châtelier's Principle \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|} \hline Variable & Type of Change & Response of System & \begin{tabular}{c} Change in \\ \end{tabular} \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{ concentration } & increase & \begin{tabular}{l} Shifts to consume some of the added \\ reactant/product. \end{tabular} & NO \\ \hline & decrease & \begin{tabular}{l} Shifts to replace some of the removed \\ reactant/product. \end{tabular} & NO \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{ temperature } & increase & \begin{tabular}{l} Shifts to consume some of the added thermal \\ energy. \end{tabular} & YES \\ \hline & decrease & \begin{tabular}{l} Shifts to replace some of the removed thermal \\ energy. \end{tabular} & YES \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{ volume } & \begin{tabular}{l} increase \\ (decrease in P) \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{l} Shifts toward the side with the larger total amount \\ of gaseous particles. \end{tabular} & NO \\ \hline & \begin{tabular}{l} decrease \\ (increase in P) \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{l} Shifts toward the side with the smaller total \\ amount of gaseous particles. \end{tabular} & NO \\ \hline \multicolumn{4}{|c|}{ Variables That Do NOT Affect Chemical Equilibria } \\ \hline catalysts & & NO effect & NO \\ \hline inert gases & & NO effect & NO \\ \hline \end{tabular}