Home /
Expert Answers /
Computer Science /
figure-4-cancer-cell-classification-review-the-table-labeled-figure-4-cancer-cell-classification-pa767
(Solved): Figure 4: Cancer Cell Classification Review the table labeled Figure 4: Cancer Cell Classification. ...
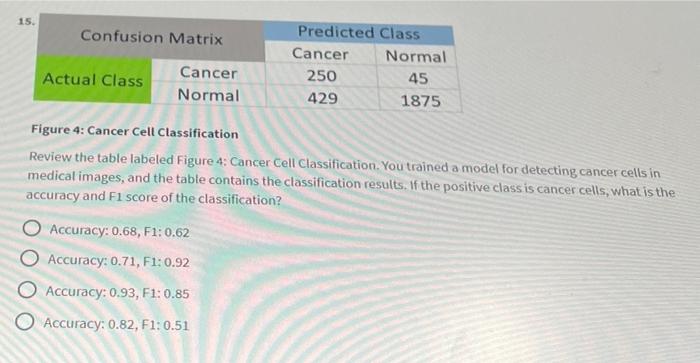

Figure 4: Cancer Cell Classification Review the table labeled Figure 4: Cancer Cell Classification. You trained a model for detecting cancer cells in medical images, and the table contains the classification results. If the positive class is cancer cells, what is the accuracy and \( \mathrm{F} 1 \) score of the classification? Accuracy: \( 0.68, \mathrm{~F} 1: 0.62 \) Accuracy: \( 0.71, \mathrm{~F} 1 ; 0.92 \) Accuracy: \( 0.93, \mathrm{~F} 1: 0.85 \) Accuracy: \( 0.82, F 1: 0.51 \)
16. You are asked to train a model for detecting cancer tumors in medical images. The hospital studies show that patients suffer more harm when a cancer tumor goes undiagnosed compared to when a benign tumor is treated for cancer. For patients to suffer less harm, which cost matrix should you use to tune your model? (F stands for Found Tumor, and \( \mathrm{N} \) stands for No Tumor.) \[ \begin{array}{l} \operatorname{Cos}((F \mid F)=0, \operatorname{Cost}(F \mid N)=1, \operatorname{Cost}(N \mid F)=1, \operatorname{Cos} t(N \mid N)=0 \\ \operatorname{Cost}(F \mid F)=0, \operatorname{Cost}(F \mid N)=20, \operatorname{Cost}(N \mid F)=2, \operatorname{Cost}(N \mid N)=0 \\ \operatorname{Cost}(F \mid F)=0, \operatorname{Cost}(F \mid N)=1, \operatorname{Cost}(N \mid F)=10, \operatorname{Cost}(N \mid N)=0 \\ \operatorname{Cost}(F \mid F)=5, \operatorname{Cost}(F \mid N)=5, \operatorname{Cost}(N \mid F)=5, \operatorname{Cost}(N \mid N)=1 \end{array} \]
Expert Answer
************** SOLUTION ************** 15. Answer: (b) Accuracy:0.