(Solved): Figure 1a shows a 10 m thick clay layer overlying a highly permeable sand layer. = 1MPa and permeabi ...
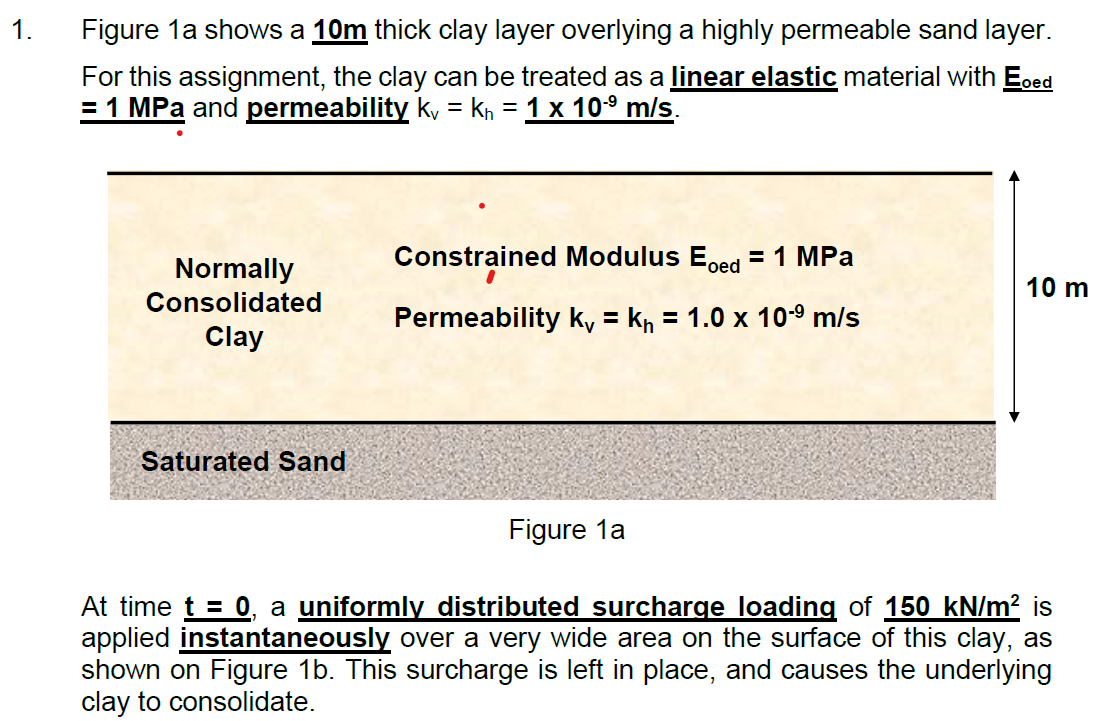
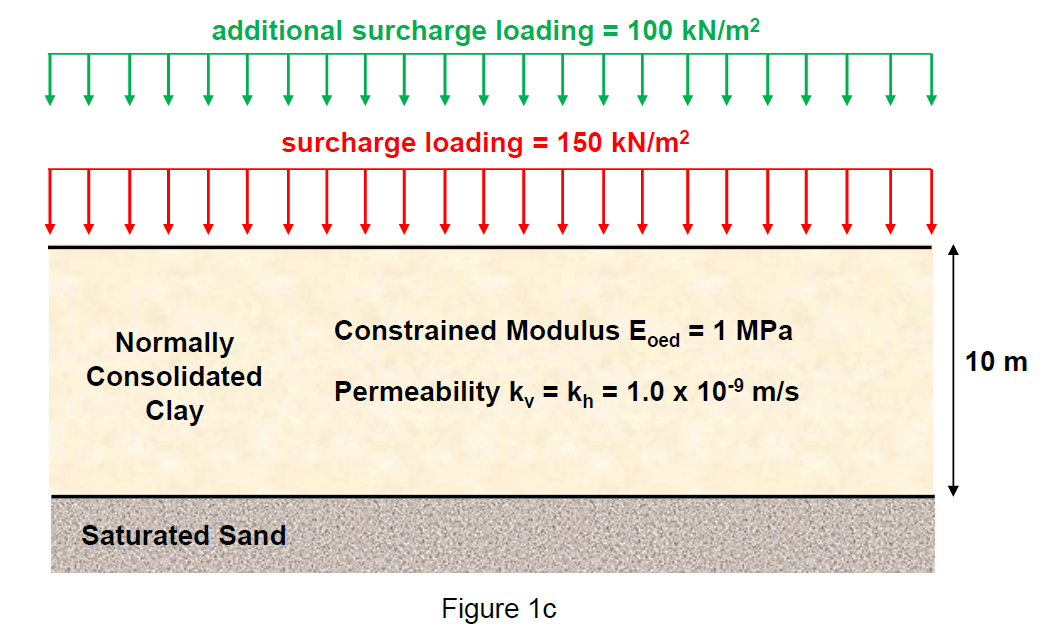
Figure 1a shows a 10 m thick clay layer overlying a highly permeable sand layer. = 1MPa and permeability k v ? =k n ? =1×10 ?9 m/s. At time t=0, a uniformly distributed surcharge loading of 150kN/m 2 is applied instantaneously over a very wide area on the surface of this clay, as shown on Figure 1 b. This surcharge is left in place, and causes the underlying clay to consolidate. At time t=2 years, an additional uniformly distributed surcharge loading of 100 kN/m 2 is applied instantaneously on top of the original 150kN/m 2 surcharge loading, as shown on Figure 1c. This brings the total surcharge loading to 250 Kpa. Estimate time (from the initial loading of the original 150 Kpa surcharge) that is needed for the clay layer to undergo settlement of 2m.