Home /
Expert Answers /
Accounting /
exercises-valuation-concepts-and-methodologies-answer-statement-15-the-cost-of-equity-may-be-also-pa285
(Solved): EXERCISES VALUATION CONCEPTS AND METHODOLOGIES ANSWER STATEMENT 15. The cost of equity may be also ...





EXERCISES
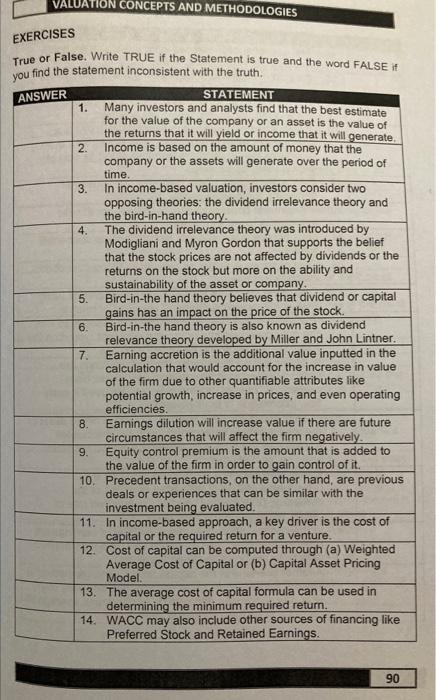
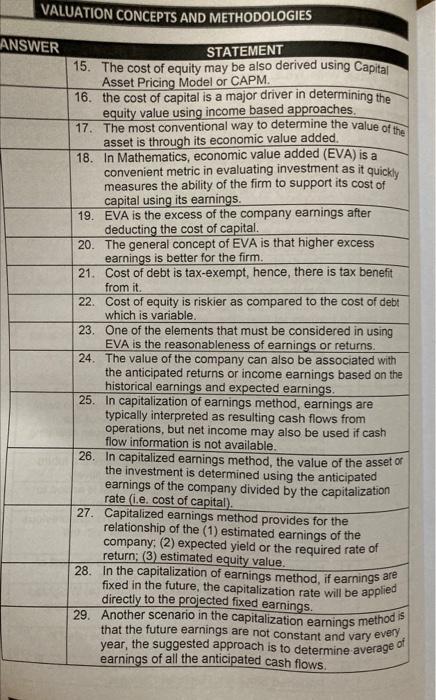
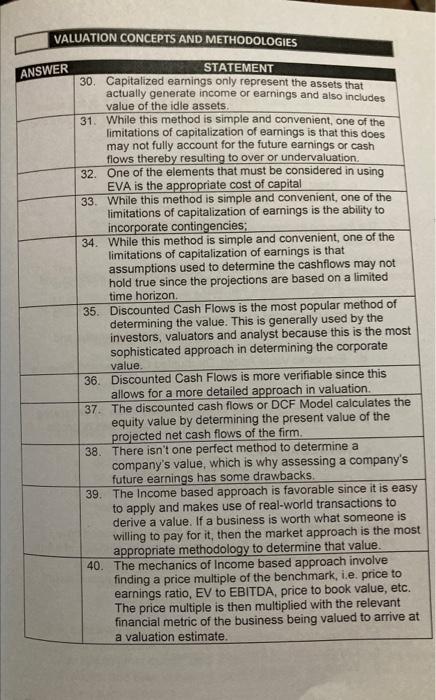
VALUATION CONCEPTS AND METHODOLOGIES ANSWER STATEMENT 15. The cost of equity may be also derived using Capital Asset Pricing Model or CAPM. 16. the cost of capital is a major driver in determining the equity value using income based approaches. 17. The most conventional way to determine the value of the asset is through its economic value added. 18. In Mathematics, economic value added (EVA) is a convenient metric in evaluating investment as it quickly measures the ability of the firm to support its cost of capital using its earnings. 19. EVA is the excess of the company earnings after deducting the cost of capital. 20. The general concept of EVA is that higher excess earnings is better for the firm. 21. Cost of debt is tax-exempt, hence, there is tax benefit from it. 22. Cost of equity is riskier as compared to the cost of debt which is variable. 23. One of the elements that must be considered in using EVA is the reasonableness of earnings or returns. 24. The value of the company can also be associated with the anticipated returns or income earnings based on the historical earnings and expected earnings. 25. In capitalization of earnings method, earnings are typically interpreted as resulting cash flows from operations, but net income may also be used if cash flow information is not available. 26. In capitalized earnings method, the value of the asset \( \alpha \) the investment is determined using the anticipated earnings of the company divided by the capitalization rate (i.e. cost of capital). 27. Capitalized earnings method provides for the relationship of the (1) estimated earnings of the company; (2) expected yield or the required rate of return; (3) estimated equity value. 28. In the capitalization of earnings method, if earnings are fixed in the future, the capitalization rate will be applied directly to the projected fixed earnings. 29. Another scenario in the capitalization earnings method is that the future earnings are not constant and vary every year, the suggested approach is to determine average of earnings of all the anticipated cash flows.
VALUATION CONCEPTS AND METHODOLOGIES
MULTIPLE CHOICE THEORIES. Write the letter of the best answer belore the number of the question or statement being answered. 1. A valuation approach that is based on the concept that the actual value of a business lies in the ability to produce revenue, profit and eventually wealth in the future. a. Income Based Valuation Approach b. Market Based Valuation Approach c. Asset Based Valuation Approach d. Liquidation Valuation Approach 2. The following methods are NOT income-based valuation technique except a. Economic Value Added, Capitalizing current earnings and discounted future earnings b. Economic Value Added, Capitalization of earnings method and discounted cashflow method c. Economic Value Added, Capitalizing past earnings and discounted cashflow approach d. Economic Value Added, Discounted Cashflow and Revenue Approach 3. Valuation approach that determines the equity value by calculating the present value of the expected future net cash flows or profits a. Revenue Approach b. Discounted Cashflows Method Approach c. Capitalization of Earnings Approach d. Economic Value Added 4. A valuation method used to estimate a firm's worth based on earnings forecasts. It uses these forecasts for the eamings of a firm and the firm's estimated terminal value at a future date, and discounts these back to the present using an appropriate discount rate. a. Revenue Approach b. Discounted Cashflows Analysis c. Capitalization of Earnings Approach d. Economic Value Added
5. The following are ways on to estimate terminal value except a. Liquidation Value Model b. Multiples Approach c. Stable Growth Approach d. Going Concern Model 6. In Income based valuation, investors consider two opposing theories a. dividend relevance theory and bird-in-hand theory b. bird-in-hand theory c. dividend irrelevance theory d. both \( b \) and \( c \) 7. The theory was introduced by Modigliani and Miller that supports the belief that the stock prices are not affected by dividends or the returns on the stock but more on the ability and sustainability of the asset or company. a. dividend relevance theory b. bird-in-hand theory c. dividend irrelevance theory d. both \( b \) and \( c \) 8. The theory believes that dividend or capital gains has an impact on the price of the stock. a. dividend relevance theory b. bird-on-hand theory c. dividend irrelevance theory. d. both \( a \) and \( b \) 9. The is also known as Income based valuation approach a. earnings approach b. market approach c. asset-based approach d. going concern approach 10. In sensitivity analysis, this factor is the additional value inputted in the calculation that would account for the increase in value of the firm due to other quantifiable attributes like potential growth, increase in prices, and even operating efficiencies. a. earning accretion
VALUATION CONCEPTS AND METHODOLUOIES b. earning dilution c. earning increments d. earning decrements 11. In sensitivity analysis, this factor will reduce value if there future circumstances that will affect the firm negatively. a. earning accretion b. earning dilution c. earning increments d. earning decrements 12. This is the amount that is added to the value of the firm in order to gain control of it. a. equity accretion b. earnings premium c. equity control premium d. additional paid in capital 13. These are the factors that can be considered to properly value the asset using income based valuation approach, except a. earning accretion or dilution b. equity accretion or dilution c. equity control premium d. precedent transaction 14. Using the income based valuation, these are previous deals or experiences that can be similar with the investment being evaluated. a. earning accretion or dilution b. equity accretion or dilution c. equity control premium d. precedent transaction 15. These transactions are considered risks that may affect further the ability to realize the projected earnings. a. earning accretion or dilution b. equity accretion or dilution c. equity control premium d. precedent transaction 16. A key factor that is used to discount the net cash flows in the future. is a. cost of equity b. cost of earnings
VALUATION CONCEPTS AND METHODOLOGIES c. cost of debt d. cost of capital 17. The cost of can be computed primarily by getting the weight of cost of sources of fund, through and a. cost of equity; weighted average cost of capital; capital asset pricing model b. cost of equity; average cost of capital; capital asset pricing model c. cost of capital; weighted average cost of capital; capital asset pricing model d. cost of capital; average cost of capital; capital asset pricing model 18. The is a calculation of a firm's in which each category of is proportionately weighted. a. weighted average cost of capital; capital; cost of capital b. weighted average cost of capital; cost of capital; capital c. average cost of capital; capital; cost of capital d. average cost of capital; cost of capital; capital 19. The beta in Capital Asset Pricing Model is a. use to represent volatility/risk of the market b. arbitrary systematic risk coefficient c. the pricing multiple used to compute for the cost of capital d. the credit spread/debt premium added to risk free rate. 20. The following statements are correct for the Economic Value Added (EVA), except: a. The most conventional way to determine the value of the asset is through its economic value added. b. Economic value added (EVA) is a convenient metric in evaluating investment as it quickly measures the ability of the firm to support its cost of capital using its earnings. c. EVA is the excess of the company's equity after deducting the cost of capital. d. The general concept here is that higher EVA is better for the firm. 21. The elements that must be considered in using EVA are as follows, except
a. Reasonableness of earnings b. Appropriate cost of capital c. Volatility of the market d. Both \( a \) and \( b \) 22. In which income based valuation method wherein the value of the asset or the investment is determined using the anticipated eamings of the company divided by the cost of capital? a. Economic Value Added (EVA) b. Capitalization of Earnings Method c. Capital Asset Pricing Method d. Discounted Cashflow Method 23. The following statements are factual discussions about Capitalization of Earnings Method except: a. In capitalization of earnings method, the value of the asset \( \alpha \) : the investment is determined using the anticipated earnings of the company divided by the cost of capital. b. You may use past earnings in the Capitalization of Earnings method for cases wherein earnings are fixed. c. The formula used in Capitalization of Earnings is actually grossing up the future earnings using capitalization rate to come up with the estimated asset value. d. Cost of Capital used in the Capitalization of Earnings method is equivalent to the expected yield or the required rate of return. 24. In capitalization of earnings method, these types of assets are not part of the computation hence need to be added to the Capitalized Earnings. a. Fixed Assets b. Idle Assets c. Current Assets d. Noncurrent Assets 25. The following statements are limitations of capitalization of eamings method, except a. this does may not fully account for the future earnings or cash flows thereby resulting to over or undervaluation b. inability to incorporate contingencies c. assumptions used to determine the cashfiows may not hold true since the projections are based on a limited time horizon. d. It is simple and convenient
Expert Answer
Multiple choice questions: Answer 1: It is the Income-based approach. Its explanation is given below: