Home /
Expert Answers /
Electrical Engineering /
electric-circuit-theory-the-superposition-theorem-for-electrical-circuits-states-that-the-response-pa945
(Solved): Electric circuit THEORY The Superposition theorem for electrical circuits states that the response ( ...
Electric circuit
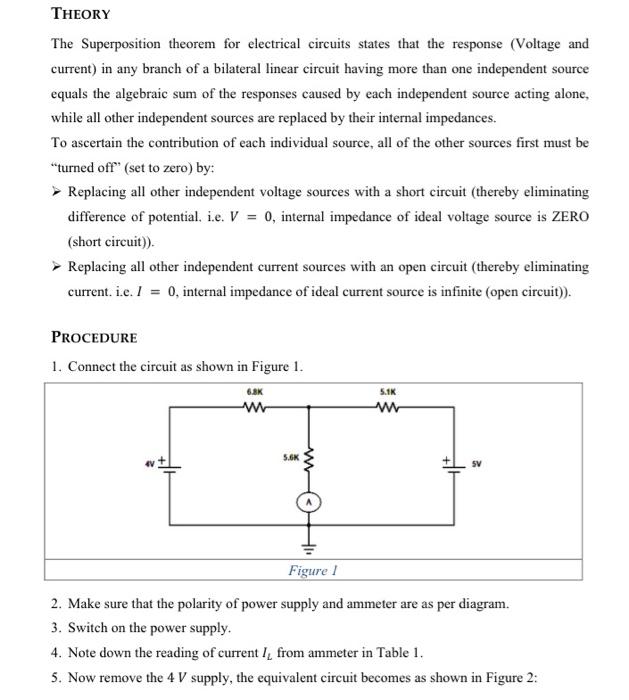
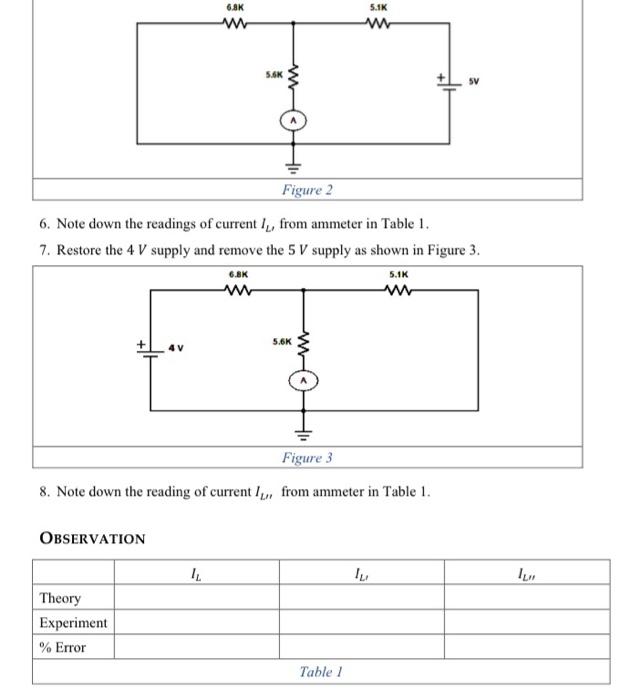


THEORY The Superposition theorem for electrical circuits states that the response (Voltage and current) in any branch of a bilateral linear circuit having more than one independent source equals the algebraic sum of the responses caused by each independent source acting alone, while all other independent sources are replaced by their internal impedances. To ascertain the contribution of each individual source, all of the other sources first must be "turned off" (set to zero) by: - Replacing all other independent voltage sources with a short circuit (thereby eliminating difference of potential. i.e. \( V=0 \), internal impedance of ideal voltage source is ZERO (short circuit)). - Replacing all other independent current sources with an open circuit (thereby eliminating current. i.e. \( I=0 \), internal impedance of ideal current source is infinite (open circuit)). ProcedURE 1. Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 1 . 2. Make sure that the polarity of power supply and ammeter are as per diagram. 3. Switch on the power supply. 4. Note down the reading of current \( I_{L} \) from ammeter in Table 1 . 5. Now remove the \( 4 V \) supply, the equivalent circuit becomes as shown in Figure 2 :
6. Note down the readings of current \( I_{L} \), from ammeter in Table 1 . 7. Restore the \( 4 \mathrm{~V} \) supply and remove the \( 5 \mathrm{~V} \) supply as shown in Figure \( 3 . \)
Expert Answer
When 4V source is disabled, First we need to find total current. In order to determine total current, we need t