Home /
Expert Answers /
Mechanical Engineering /
design-of-a-geothermal-heating-system-nbsp-you-are-tasked-to-design-a-closed-loop-geothermal-syst-pa659
(Solved): Design of a Geothermal Heating System. You are tasked to design a closed loop geothermal syst ...
Design of a Geothermal Heating System.
You are tasked to design a closed loop geothermal system for a house. Based upon heating requirements, you have selected a unit that requires a maximum power of 2.5 kW and has a coefficient of performance of 4 when used as a heat pump.
(24 points) Design of a Geothermal Heating System You are tasked to design a closed loop geothermal system for a house. Based upon heating requirements, you have selected a unit that requires a maximum power of \( 2.5 \mathrm{~kW} \) and has a coefficient of performance of 4 when used as a heat pump. (a) (7 points) What is the maximum rate of heat transfer to the house in \( \mathrm{kW} \) (also convert your result to Btu/hr, which is the standard unit for heating systems)?
(b) ( 7 points) At what rate is heat extracted from the ground in \( \mathrm{kW} \) ?
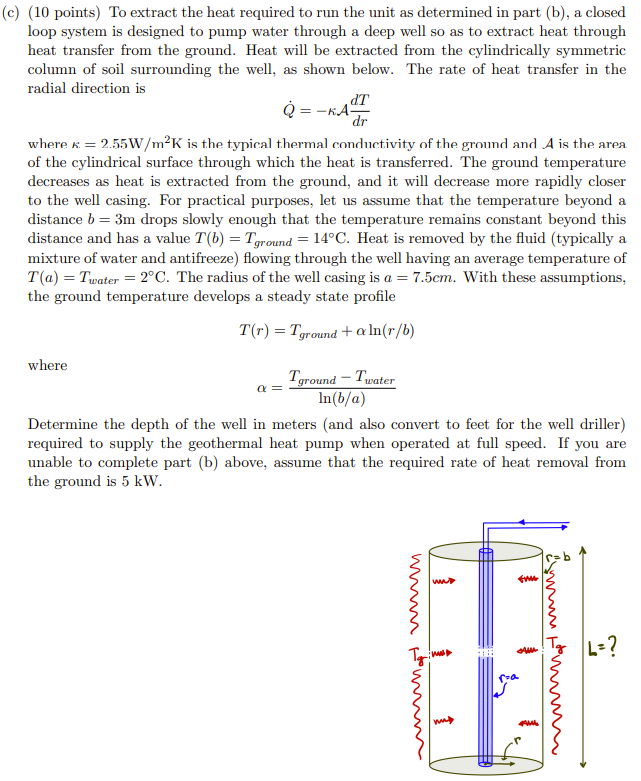
c) (10 points) To extract the heat required to run the unit as determined in part (b), a closed loop system is designed to pump water through a deep well so as to extract heat through heat transfer from the ground. Heat will be extracted from the cylindrically symmetric column of soil surrounding the well, as shown below. The rate of heat transfer in the radial direction is \[ \dot{Q}=-\kappa \mathcal{A} \frac{d T}{d r} \] where \( \kappa=2.55 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m}^{2} \mathrm{~K} \) is the typical thermal conductivity of the ground and \( \mathcal{A} \) is the area of the cylindrical surface through which the heat is transferred. The ground temperature decreases as heat is extracted from the ground, and it will decrease more rapidly closer to the well casing. For practical purposes, let us assume that the temperature beyond a distance \( b=3 \mathrm{~m} \) drops slowly enough that the temperature remains constant beyond this distance and has a value \( T(b)=T_{\text {ground }}=14^{\circ} \mathrm{C} \). Heat is removed by the fluid (typically a mixture of water and antifreeze) flowing through the well having an average temperature of \( T(a)=T_{\text {water }}=2^{\circ} \mathrm{C} \). The radius of the well casing is \( a=7.5 \mathrm{~cm} \). With these assumptions, the ground temperature develops a steady state profile \[ T(r)=T_{\text {ground }}+\alpha \ln (r / b) \] where \[ \alpha=\frac{T_{\text {ground }}-T_{\text {water }}}{\ln (b / a)} \] Determine the depth of the well in meters (and also convert to feet for the well driller) required to supply the geothermal heat pump when operated at full speed. If you are unable to complete part (b) above, assume that the required rate of heat removal from the ground is \( 5 \mathrm{~kW} \).
Expert Answer
data : work W = 2.5 kW heat transfer to house Qh= ? COP = 4 heat pump working on Carnot cycle will have max heat transfer rate WQhQl