Home /
Expert Answers /
Advanced Math /
d-bryant-angles-123-xyz-123-textbook-39-s-notation-these-angles-are-a-pa267
(Solved): D. Bryant Angles (123):xyz(123) - Textbook's Notation These angles are a ...
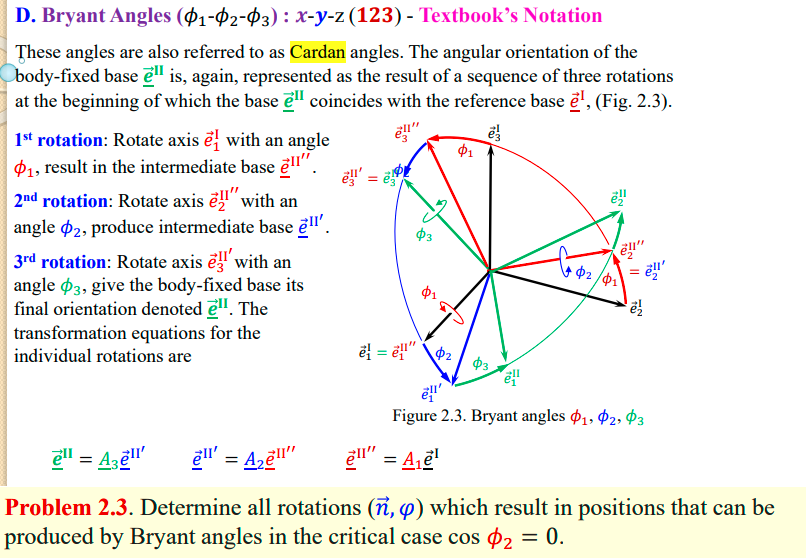
D. Bryant Angles - Textbook's Notation These angles are also referred to as Cardan angles. The angular orientation of the body-fixed base is, again, represented as the result of a sequence of three rotations at the beginning of which the base coincides with the reference base , (Fig. 2.3). rotation: Rotate axis with an angle , result in the intermediate base . rotation: Rotate axis with an angle , produce intermediate base . rotation: Rotate axis with an angle , give the body-fixed base its final orientation denoted . The transformation equations for the individual rotations are Figure 2.3. Bryant angles Problem 2.3. Determine all rotations which result in positions that can be produced by Bryant angles in the critical case .
Expert Answer
In the case where we are considering the critic...