Home /
Expert Answers /
Civil Engineering /
consider-the-momentum-flux-and-external-forces-at-the-exit-plane-a-what-is-the-gage-pressure-at-pa827
(Solved): Consider the momentum flux and external forces at the exit plane. (a) What is the gage pressure at ...

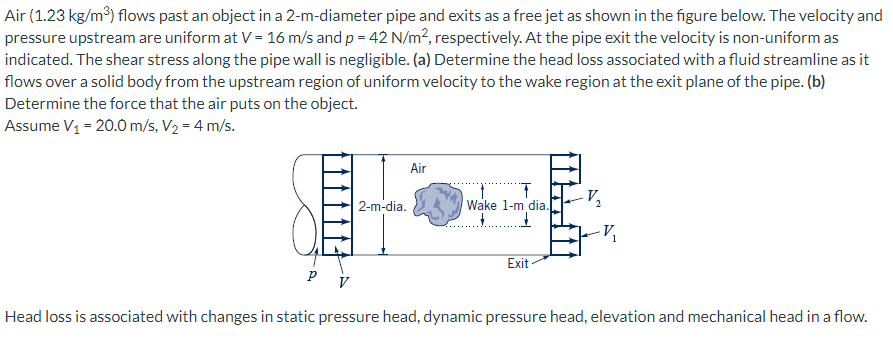
Consider the momentum flux and external forces at the exit plane. (a) What is the gage pressure at the exit plane? (b) What is the force due to pressure at the exit plane? (c) What is the uniform velocity at the exit plane in the wake region of the object? (d) What is the cross-sectional area associated with this wake region velocity? (e) What is the momentum flux at the exit plane in the wake region of the object? (f) What is the uniform velocity at the exit plane in the annular space surrounding the wake of the object? (g) What is the cross-sectional area associated with this annular velocity? (h) What is the momentum flux at the exit plane in the annular space surrounding the wake of the object? (i) What is the magnitude of the force of the air on the object? (j) What is the direction of the force of the air on the object? (1 depicts right, 0 - otherwise)
flows past an object in a 2 -m-diameter pipe and exits as a free jet as shown in the figure below. The velocity and pressure upstream are uniform at and , respectively. At the pipe exit the velocity is non-uniform as indicated. The shear stress along the pipe wall is negligible. (a) Determine the head loss associated with a fluid streamline as it flows over a solid body from the upstream region of uniform velocity to the wake region at the exit plane of the pipe. (b) Determine the force that the air puts on the object. Assume . Head loss is associated with changes in static pressure head, dynamic pressure head, elevation and mechanical head in a flow.