Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemical Engineering /
consider-a-liquid-mixture-of-chcl3-component-a-and-ch2cl2-component-b-with-xb-0-7-pa177
(Solved): Consider a liquid mixture of CHCl3 (component A ) and CH2Cl2 (component B ) with xB=0.7 ...
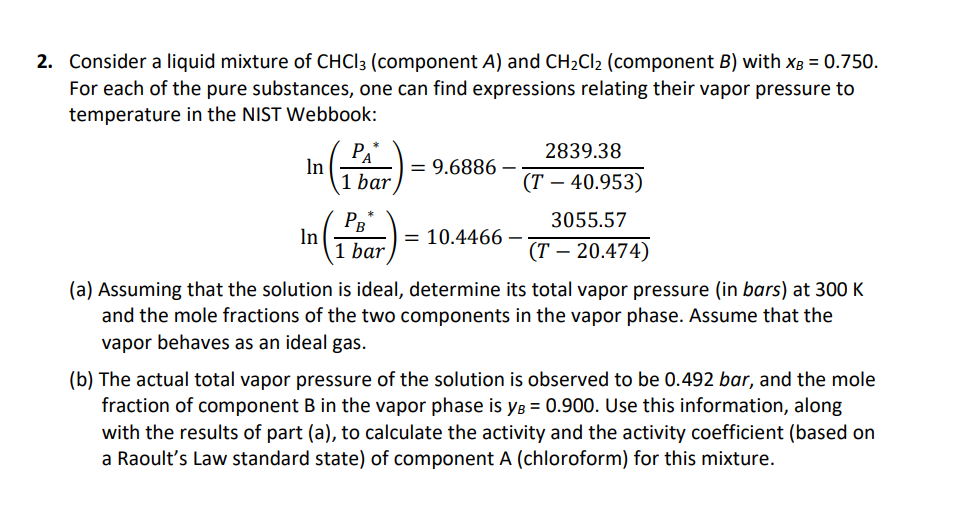
Consider a liquid mixture of (component ) and (component ) with . For each of the pure substances, one can find expressions relating their vapor pressure to temperature in the NIST Webbook: (a) Assuming that the solution is ideal, determine its total vapor pressure (in bars) at and the mole fractions of the two components in the vapor phase. Assume that the vapor behaves as an ideal gas. (b) The actual total vapor pressure of the solution is observed to be 0.492 bar, and the mole fraction of component in the vapor phase is . Use this information, along with the results of part (a), to calculate the activity and the activity coefficient (based on a Raoult's Law standard state) of component A (chloroform) for this mixture.