Home /
Expert Answers /
Advanced Physics /
calculations-constant-mass-increasing-net-force-calculate-the-theoretical-acceleration-when-mass-pa589
(Solved): Calculations: Constant Mass, Increasing Net Force Calculate the theoretical acceleration when mass ...
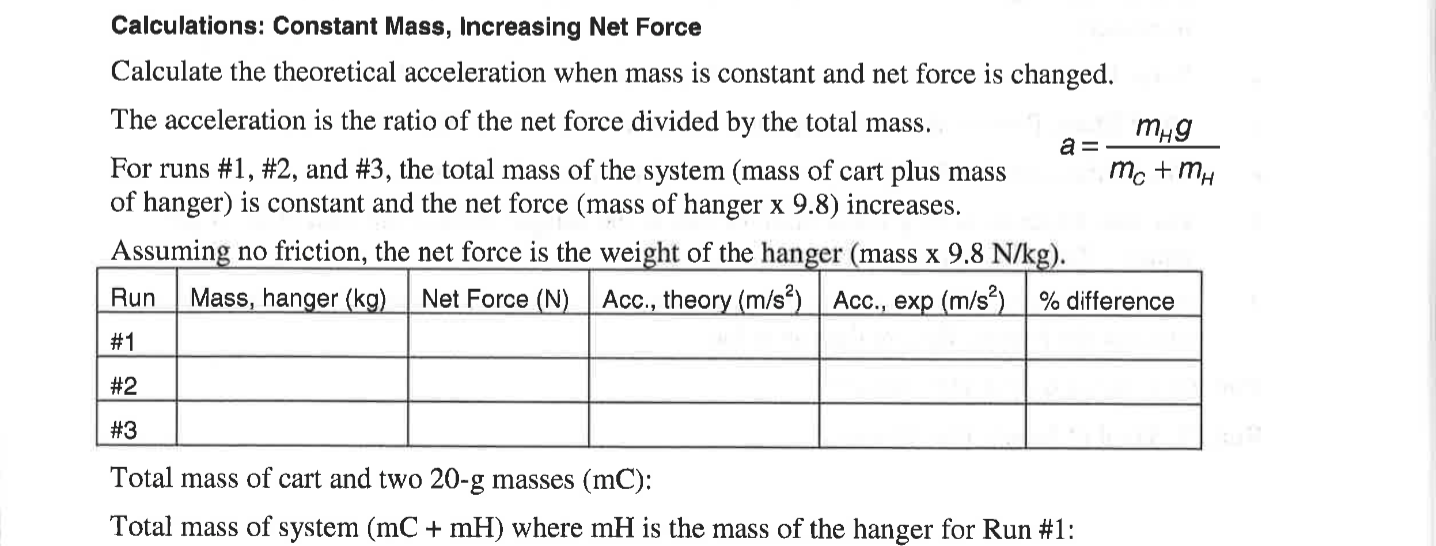
Calculations: Constant Mass, Increasing Net Force Calculate the theoretical acceleration when mass is constant and net force is changed. The acceleration is the ratio of the net force divided by the total mass. For runs \( \# 1, \# 2 \), and \( \# 3 \), the total mass of the system (mass of cart plus mass \( \quad a=\frac{m_{H} g}{m_{C}+m_{H}} \) of hanger) is constant and the net force (mass of hanger \( x \) 9.8) increases. Assuming no friction, the net force is the weight of the hanger (mass \( \times 9.8 \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{kg} \) ). Total mass of cart and two \( 20-\mathrm{g} \) masses \( (\mathrm{mC}) \) : Total mass of system \( (\mathrm{mC}+\mathrm{mH}) \) where \( \mathrm{mH} \) is the mass of the hanger for Run #1:
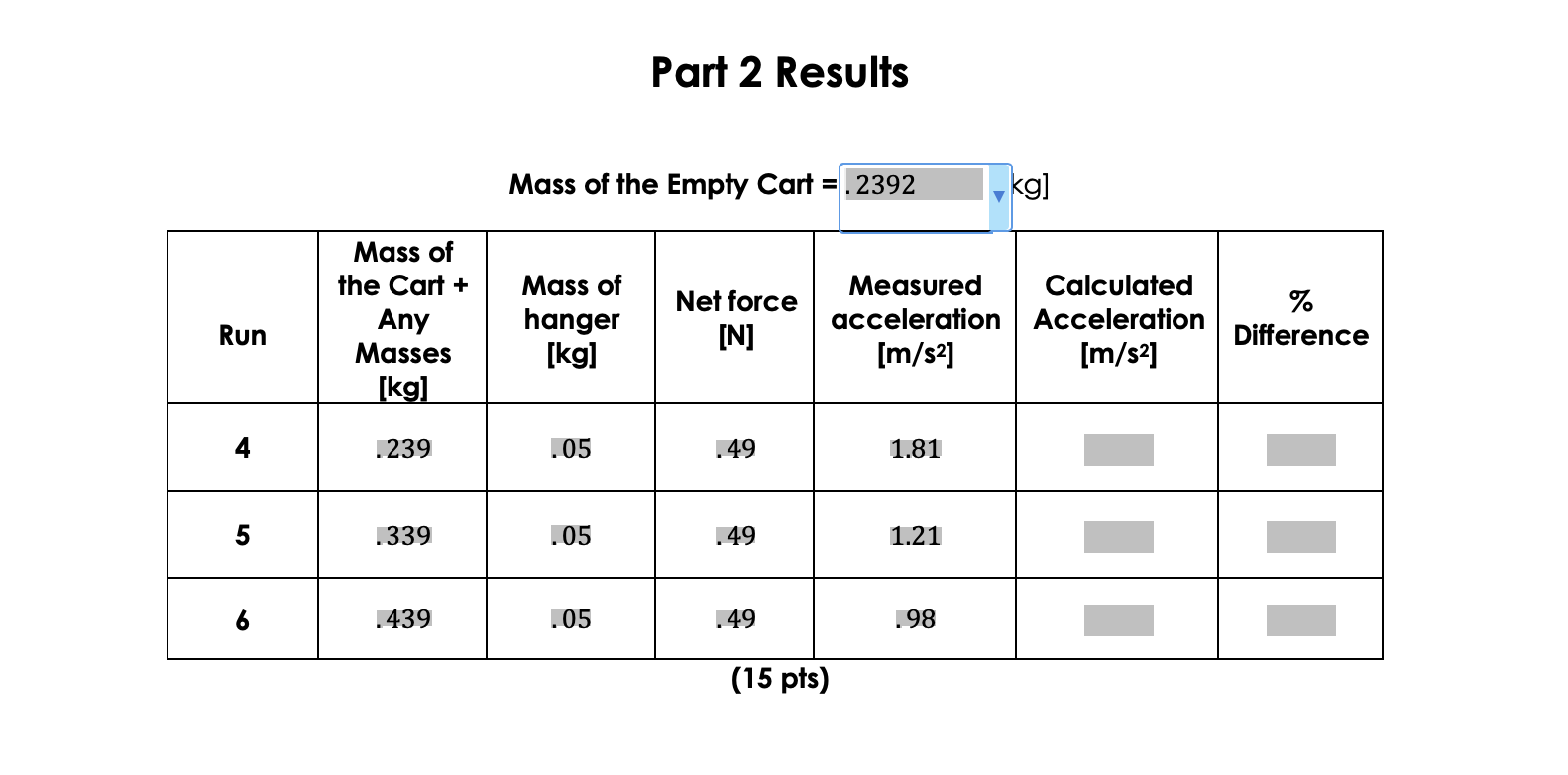
Mass of the Empty Cart =
Expert Answer
The equation for theoretical acceleration is a=mHgmC+mH where mHis the mass of hanger mCis the mss of cart and g=9.8 m/s2is the acceleration due to gr