Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemistry /
br-ch3-bra-ch3-hc-ch2cl2-h3c-br-electrophilic-addition-of-bromine-brz-to-alkenes-yields-a-1-2-pa655
(Solved): Br CH3 Bra CH3 HC/ CH2Cl2 H3C Br Electrophilic addition of bromine, Brz, to alkenes yields a 1,2 ...
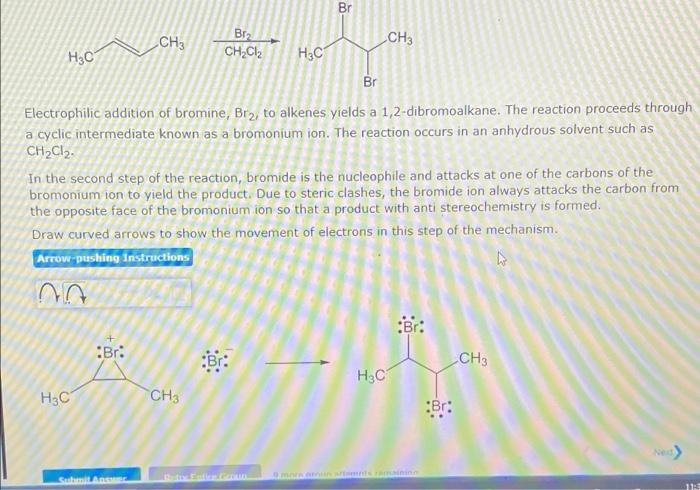
Br CH3 Bra CH3 H?C/ CH2Cl2 H3C Br Electrophilic addition of bromine, Brz, to alkenes yields a 1,2-dibromoalkane. The reaction proceeds through a cyclic intermediate known as a bromonium ion. The reaction occurs in an anhydrous solvent such as CH2Cl2. In the second step of the reaction, bromide is the nucleophile and attacks at one of the carbons of the bromonium ion to yield the product. Due to steric clashes, the bromide ion always attacks the carbon from the opposite face of the bromonium ion so that a product with anti stereochemistry is formed. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions C :Br: Bri -CH? H3C H3C CH3 Br: Sunil
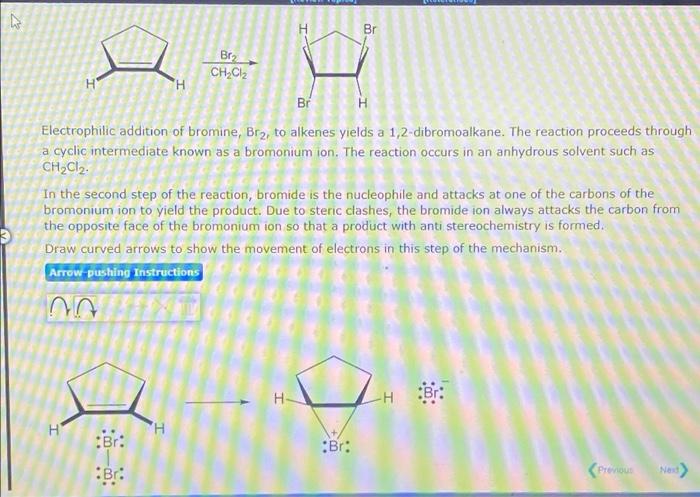
M Br BE2 CH2Cl2 H ? Br Electrophilic addition of bromine, Br?, to alkenes yields a 1,2-dibromoalkane. The reaction proceeds through a cyclic intermediate known as a bromonium ion. The reaction occurs in an anhydrous solvent such as CH2Cl2. In the second step of the reaction, bromide is the nucleophile and attacks at one of the carbons of the bromonium ion to yield the product. Due to steric clashes, the bromide ion always attacks the carbon from the opposite face of the bromonium ion so that a product with anti stereochemistry is formed. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow pushing Instructions 3 H H Br: -H H H :Br: •Br: :Br: Previous Nov
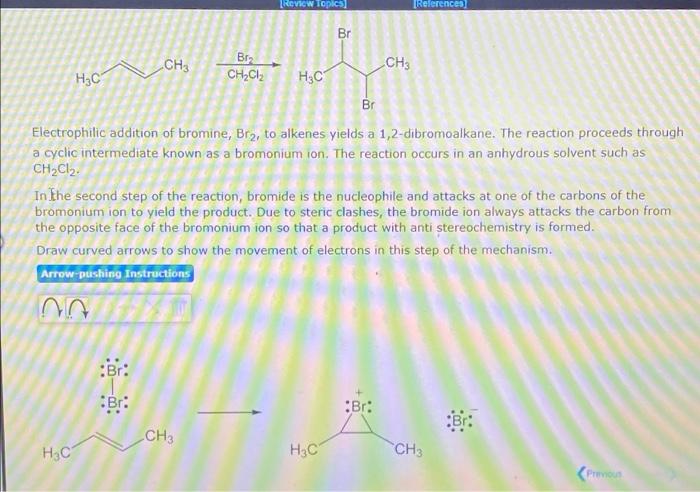
[Review Topics References Br CH3 Bru CH3 H3C CH2CIz H3C Br Electrophilic addition of bromine, Br?, to alkenes yields a 1,2-dibromoalkane. The reaction proceeds through a cyclic intermediate known as a bromonium ion. The reaction occurs in an anhydrous solvent such as CH2Cl2. In the second step of the reaction, bromide is the nucleophile and attacks at one of the carbons of the bromonium ion to yield the product. Due to steric clashes, the bromide ion always attacks the carbon from the opposite face of the bromonium ion so that a product with anti stereochemistry is formed. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions in :Br: Br: Br: CH3 ?4? ?4? CH3 Pronoun
Expert Answer
Qus1+3 :: trans-alkene + Br2 :::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::