Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemistry /
at-equilibrium-the-concentrations-of-reactants-and-products-can-be-predicted-using-the-equ-pa420
(Solved): At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products can be predicted using the equ ...

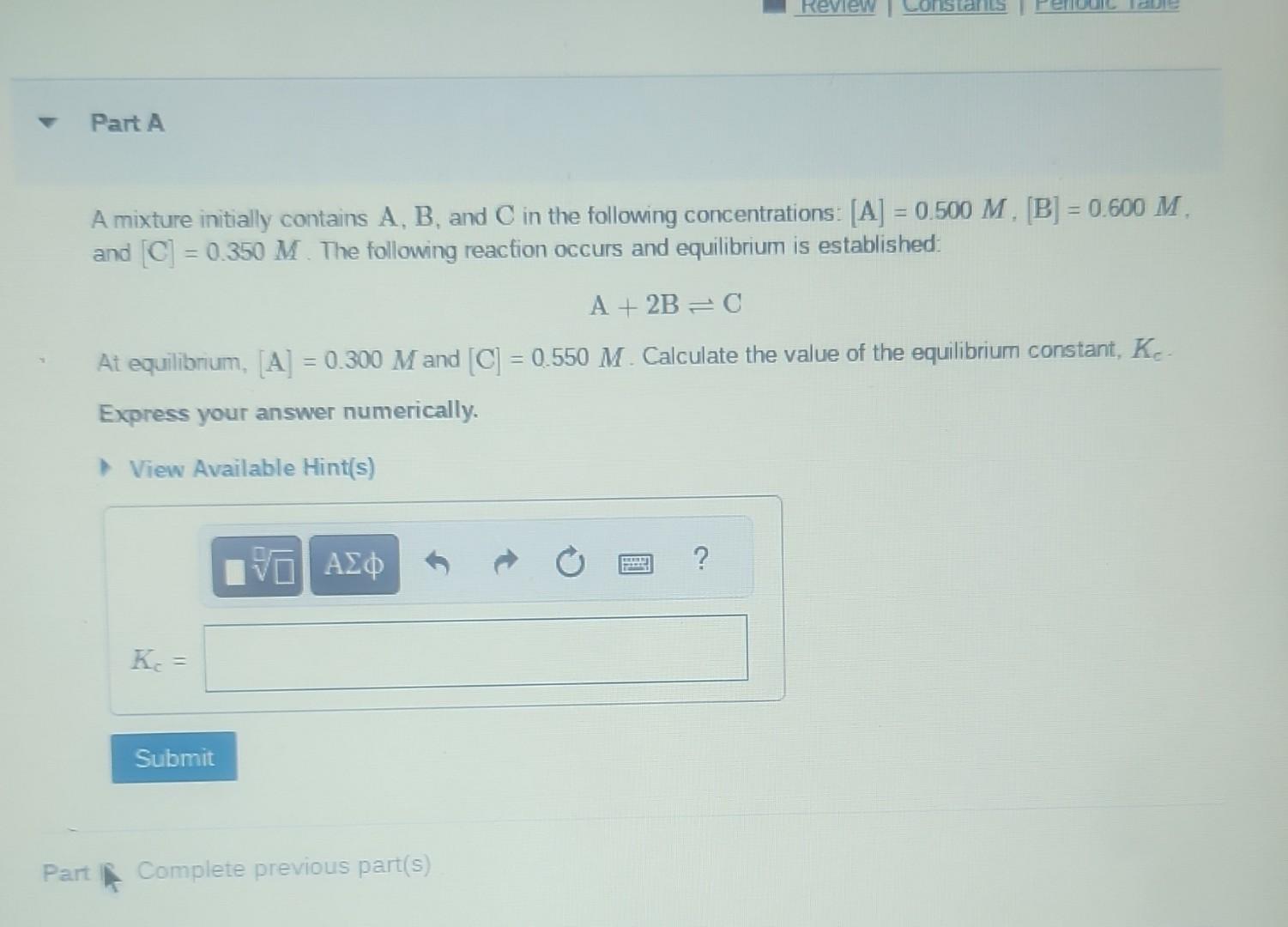
At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products can be predicted using the equilibrium constant, , which is a mathematical expression based on the chemical equation. For example, in the reaction where , and are the stoichiometric coefficients, the equilibrium constant is where , and are the equilibrium concentrations. If the reaction is not at equilibrium, the quantity can still be calculated, but it is called the reaction quotient, , instead of the equilibrium constant, . where each concentration is measured at some arbitrary time .
A mixture initially contains , and in the following concentrations: , and . The following reaction occurs and equilibrium is established: At equilibrium, and . Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant, . Express your answer numerically.