Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemical Engineering /
air-an-ideal-gas-passes-through-the-turbine-and-heat-exchanger-assembly-shown-schematically-the-p-pa635
(Solved): Air, an ideal gas, passes through the turbine and heat exchanger assembly shown schematically. The p ...
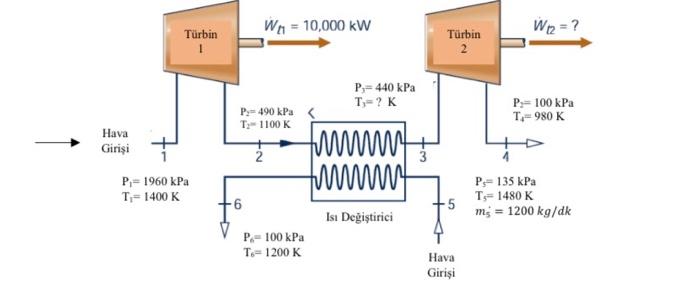
Air, an ideal gas, passes through the turbine and heat exchanger assembly shown schematically. The process takes place in a stable state and the operating conditions are given in the figure. In the case where there is no heat transfer and the change of kinetic energy and potential energy is neglected, a) T3 temperature (K) and mass flow rate of air passing through turbines (kg/s), b) The power produced in the second turbine (kW) and the amount of heat transferred in the heat exchanger (kW) calculate.
Expert Answer
To solve the problem, we can apply the conservation equations for an ideal gas undergoing a steady-state process. We'll start by analyzing the conditions at each stage and then use the equations to find the required values.Given data: Inlet Conditions: P1 = 1960 kPa T1 = 1400 KTurbine 1 Exit Conditions: P2 = 490 kPa T2 = 1100 KTurbine 2 Exit Conditions: P3 = 100 kPa T3 = 1200 K (to be determined)Heat Exchanger: Turbine 2 Inlet Conditions: P4 = 135 kPa T4 = 1480 K m = 1200 kg/minNow let's solve for the unknowns: