Home /
Expert Answers /
Mechanical Engineering /
a-rectangular-plate-simply-supported-at-all-edges-is-loaded-by-a-uniformly-distributed-loading-q-pa184
(Solved): A rectangular plate, simply supported at all edges, is loaded by a uniformly distributed loading q ...
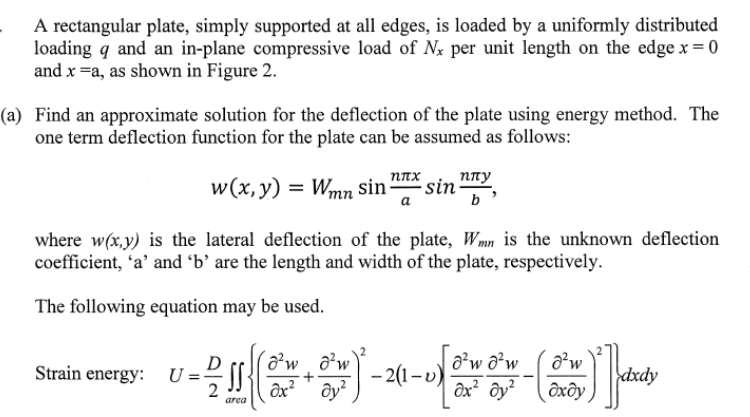
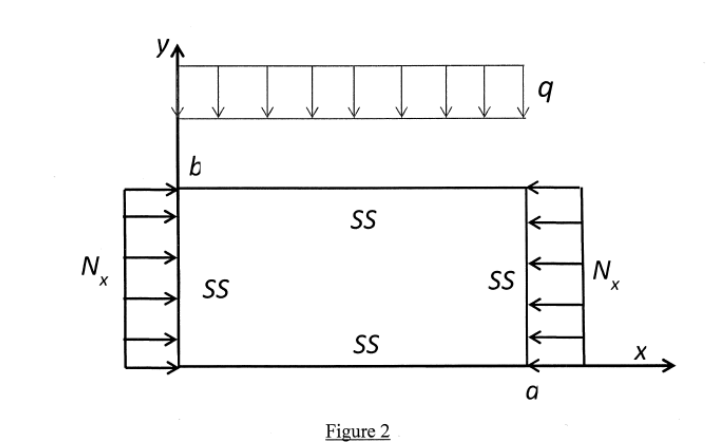
A rectangular plate, simply supported at all edges, is loaded by a uniformly distributed loading and an in-plane compressive load of per unit length on the edge and , as shown in Figure 2 . Find an approximate solution for the deflection of the plate using energy method. The one term deflection function for the plate can be assumed as follows: where is the lateral deflection of the plate, is the unknown deflection coefficient, ' ' and ' ' are the length and width of the plate, respectively. The following equation may be used. Strain energy:
A rectangular plate, simply supported at all edges, is loaded by a uniformly distributed loading and an in-plane compressive load of per unit length on the edge and , as shown in Figure 2 . Find an approximate solution for the deflection of the plate using energy method. The one term deflection function for the plate can be assumed as follows: where is the lateral deflection of the plate, is the unknown deflection coefficient, ' ' and ' ' are the length and width of the plate, respectively. The following equation may be used. Strain energy:
Figure 2