Home /
Expert Answers /
Statistics and Probability /
a-fair-coin-is-tossed-two-times-and-the-events-a-and-b-are-defined-as-shown-below-co-pa111
(Solved): A fair coin is tossed two times, and the events \( A \) and \( B \) are defined as shown below. Co ...
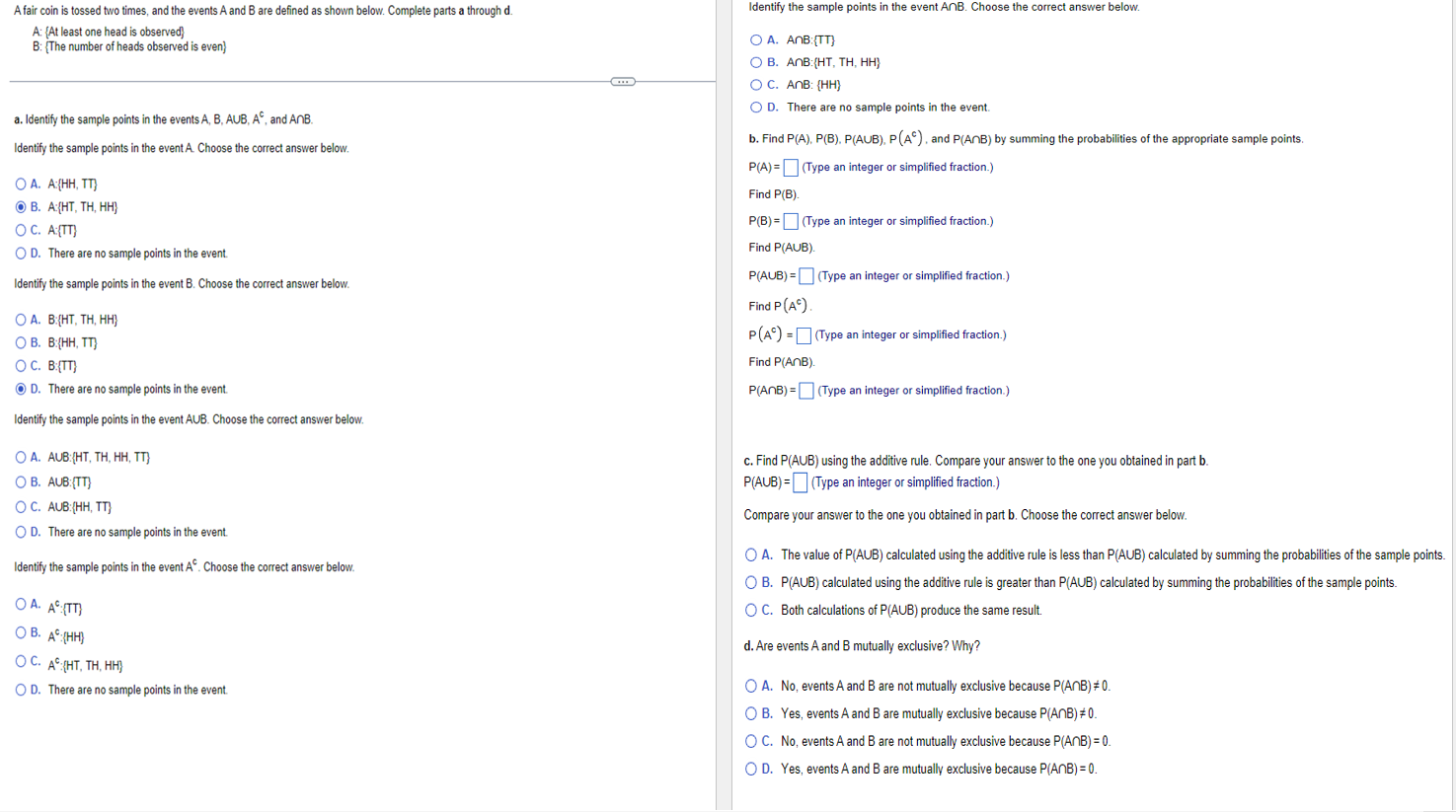
A fair coin is tossed two times, and the events \( A \) and \( B \) are defined as shown below. Complete parts a through \( \mathrm{d} \). A: \{At least one head is observed\} A. \( \mathrm{A} \cap \mathrm{B}:\{\mathrm{TT}\} \) B. \( A \cap B:\{H T, T H, H H\} \) C. \( A \cap B:\{\mathrm{HH}\} \) a. Identify the sample points in the events \( A, B, A \cup B, A^{C} \), and \( A \cap B \). D. There are no sample points in the event. Identify the sample points in the event \( \mathrm{A} \). Choose the correct answer below. b. Find \( P(A), P(B), P(A \cup B), P\left(A^{c}\right) \), and \( P(A \cap B) \) by summing the probabilities of the appropriate sample points. A. \( A:\{H H, T T\} \) \( P(A)= \) (Type an integer or simplified fraction.) ( B). A:\{HT, TH, HH\} Find \( P(B) \). C. \( A:\{T T\} \) \( P(B)=\square \) (Type an integer or simplified fraction.) ). There are no sample points in the event. Find \( P(A \cup B) \). Identify the sample points in the event B. Choose the correct answer below. \( \mathrm{P}(\mathrm{A} \cup \mathrm{B})=\quad \) (Type an integer or simplified fraction.) A. \( \mathrm{B}:\{\mathrm{HT}, \mathrm{TH}, \mathrm{HH}\} \) Find \( P\left(A^{c}\right) \). B. \( B:\{H H, T T\} \) \( P\left(A^{c}\right)=\quad \) (Type an integer or simplified fraction.) E. B:\{TT\} Find \( P(A \cap B) \). ). There are no sample points in the event. \( P(A \cap B)=\quad \) (Type an integer or simplified fraction.) Identify the sample points in the event AUB. Choose the correct answer below. A. AUB:\{HT, TH, HH, TT c. Find \( P(A \cup B) \) using the additive rule. Compare your answer to the one you obtained in part \( b \). B. \( A \cup B:\{T T\} \) \( P(A \cup B)=\quad \) (Type an integer or simplified fraction.) ¿. AUB:\{HH,TT\} Compare your answer to the one you obtained in part \( \mathbf{b} \). Choose the correct answer below. ). There are no sample points in the event. A. The value of \( P(A \cup B) \) calculated using the additive rule is less than \( P(A \cup B) \) calculated by summing the probabilities of the sample points. Identify the sample points in the event \( \mathrm{A}^{\mathrm{c}} \). Choose the correct answer below. B. \( P(A \cup B) \) calculated using the additive rule is greater than \( P(A \cup B) \) calculated by summing the probabilities of the sample points. A. \( A^{c}:\{T T\} \) C. Both calculations of \( P(A \cup B) \) produce the same result. B. \( A^{c}:\{H H\} \) d. Are events \( A \) and \( B \) mutually exclusive? Why? ¿. \( A^{\mathrm{C}}:\{\mathrm{HT}, \mathrm{TH}, \mathrm{HH}\} \) D. There are no sample points in the event. A. No, events \( A \) and \( B \) are not mutually exclusive because \( P(A \cap B) \neq 0 \). B. Yes, events \( A \) and \( B \) are mutually exclusive because \( P(A \cap B) \neq 0 \). C. No, events \( A \) and \( B \) are not mutually exclusive because \( P(A \cap B)=0 \). D. Yes, events \( A \) and \( B \) are mutually exclusive because \( P(A \cap B)=0 \).
Expert Answer
A fair coin is tossed two times. Sample Space S={HH,HT,TH,TT} A: Atleast one head is observed : {HH,HT,TH} B: The number of heads observed is even : {