Home /
Expert Answers /
Electrical Engineering /
a-calculate-the-theoretical-values-for-f-r-e-s-q-and-b-w-using-the-nominal-compone-pa428
(Solved): a. Calculate the theoretical values for \( f_{r e s}, Q \), and \( B W \) using the nominal compone ...

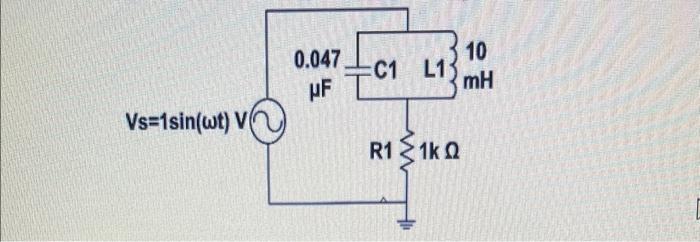
a. Calculate the theoretical values for \( f_{r e s}, Q \), and \( B W \) using the nominal component values shown in Fig. 2, the nominal value of \( R_{s} \) determined in prior experiments, and \( R_{\text {coil }}=0 \) The use of \( R_{\text {coil }}=0 \) is based on the assumption of an ideal inductor. If \( R_{\text {coil }}>0 \) for the actual inductor used in the experiment, use analysis of the equations to explain how the experimental values for \( f_{\text {res }}, Q \), and \( B W \) would be expected to differ from the theoretical values that were calculated using \( R_{c o l}=0 \). b. Prepare a sketch of the circuit that you are to build. Determine which instruments are needed to measure \( V_{R 1} \) for determining the frequency response. On the sketch, show the circuit connections for all instruments. c. For \( R_{c o i}=0 \), perform Spice simulations to compute \( V_{R 1} \) vs. frequency and \( V_{C}=V_{L} \) vs. frequency. Plot the following on the same set of axes using a \( \log -\log \) scale: \( V_{R I} \) vs. frequency and \( V_{c}=V_{1} \) vs. frequency. d. Redraw the circuit of Fig. 2 to show \( R_{S} \) and \( R_{\text {coll. }} \). Taking \( R_{S} \) and \( R_{\text {coil }} \) into account, use a voltage divider approach to derive an expression for \( V R I \) function of frequency. e. For \( V_{n 1} \), compare Spice simulation results against hand calculations to verify that the simulations are correct. Make the hand calculations using \( R_{\text {sol }}=0 \) in the expression for \( V_{R J} \). Check \( V_{R i} \) at two decades below the resonant frequency, at the resonant frequency, at frequencies that correspond to the expected half-power points, and at two decades above the resonant frequency. f. The theoretical frequency response of \( V_{2} \) ivas computed for \( R_{\text {ceu }}=0 \). If \( R_{e s u}>0 \) for the actual inductor used in the experiment, use analysis of the expression derived for \( V_{k:} \) to explain how the experimental values for the frequency response would differ from the theory.
Expert Answer
QUESTION Calculate the theoretical values for f m . Q and BW using the nominal component values shown