Home /
Expert Answers /
Physics /
9-problem-2-a-planar-surface-has-area-a-and-unit-normal-n-this-planar-surface-resides-in-a-r-pa573
(Solved): (9\%) Problem 2: A planar surface has area A and unit normal n^. This planar surface resides in a r ...

(9\%) Problem 2: A planar surface has area and unit normal . This planar surface resides in a region where the uniform electric field may be expressed as , where is its magnitude, and is its direction. A 33\% Part (a) Which statement best explains the orientation of the surface relative to the electric field that produces the maximum electric flux, ? Because the flux depends upon the cosine of the angle, the maximum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , points in the same direction as the electric field, Because the flux depends upon the sine of the angle, the maximum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , points in the same direction as the electric field, Because the flux depends upon the cosine of the angle, the maximum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , is perpendicular to the electric field, Because the flux depends upon the cosine of the angle, the maximum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , points in the direction opposite to the electric field, . Because the flux depends upon the sine of the angle, the maximum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , points in the direction opposite to the electric field, . Because the flux depends upon the sine of the angle, the maximum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , is perpendicular to the electric field, . Because the flux is a scalar quantity, it does not depend upon the orientation of the surface, so every orientation is equivalent.
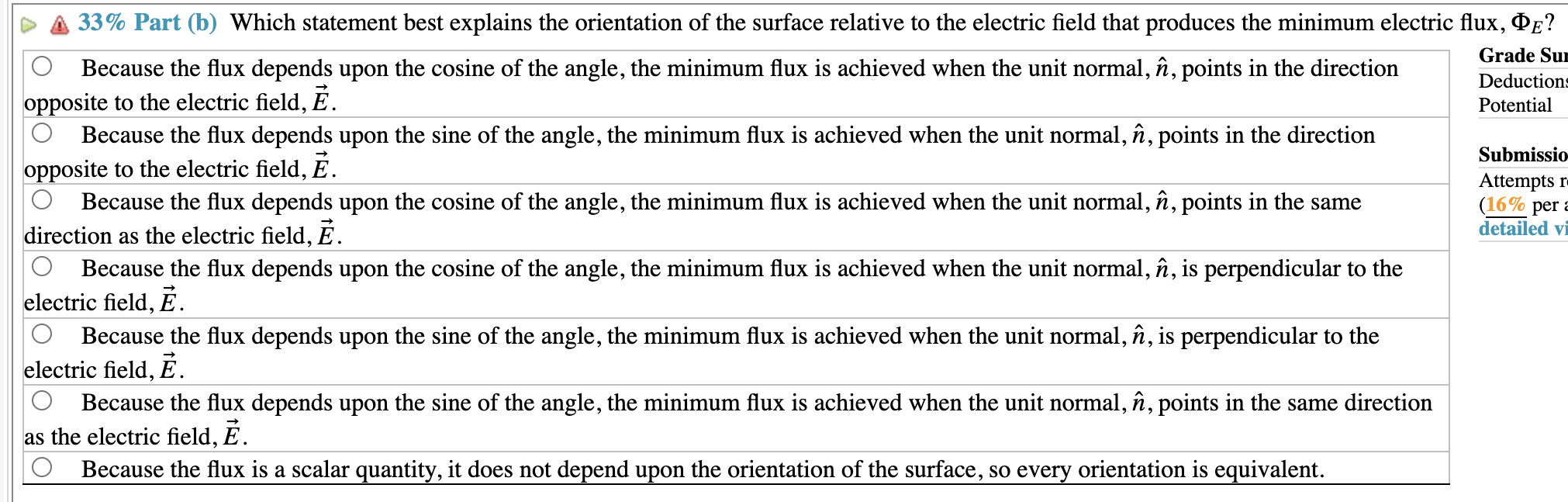
Because the flux depends upon the cosine of the angle, the minimum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , points in the direction opposite to the electric field, Because the flux depends upon the sine of the angle, the minimum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , points in the direction opposite to the electric field, Because the flux depends upon the cosine of the angle, the minimum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , points in the same direction as the electric field, Because the flux depends upon the cosine of the angle, the minimum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , is perpendicular to the electric field, Because the flux depends upon the sine of the angle, the minimum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , is perpendicular to the electric field, Because the flux depends upon the sine of the angle, the minimum flux is achieved when the unit normal, , points in the same direction as the electric field, Because the flux is a scalar quantity, it does not depend upon the orientation of the surface, so every orientation is equivalent.