Home /
Expert Answers /
Economics /
7-correcting-for-negative-externalities-taxes-versus-tradable-permits-nuclear-faclities-emit-rad-pa228
(Solved): 7. Correcting for negative externalities - Taxes versus tradable permits Nuclear faclities emit rad ...
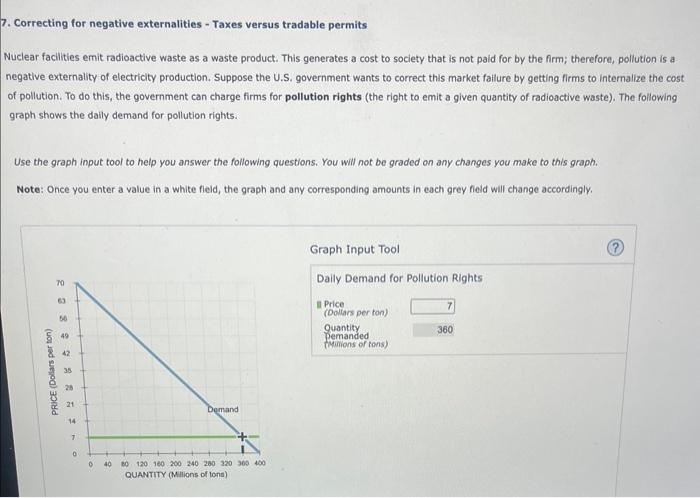
7. Correcting for negative externalities - Taxes versus tradable permits Nuclear faclities emit radioactive waste as a waste product. This generates a cost to society that is not paid for by the firm; therefore, pollution is a negative externality of electricity production. Suppose the U.S. government wants to correct this market fallure by getting firms to internalize the cost of pollution. To do this, the government can charge firms for pollution rights (the right to emit a given quantity of radioactive waste). The following graph shows the daily demand for pollution rights. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Graph input Tool
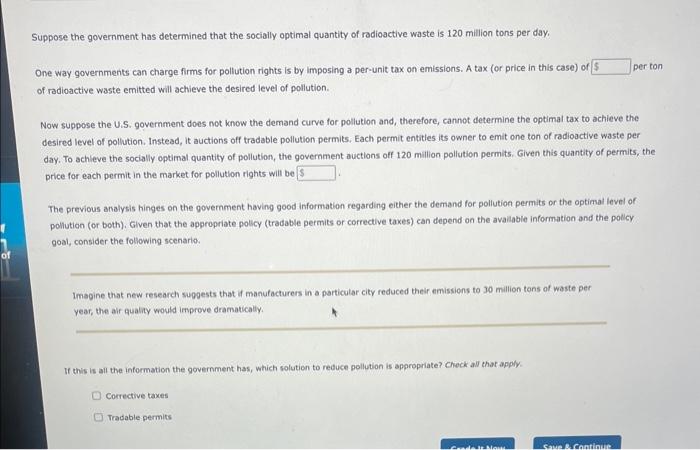
uppose the government has determined that the socially optimal quantity of radioactive waste is 120 million tons per day. One way governments can charge firms for pollution rights is by imposing a per-unit tax on emissions. A tax (or price in this case) of per ton of radioactive waste emitted will achieve the desired level of pollution. Now suppose the U.S. government does not know the demand curve for pollution and, therefore, cannot determine the optimal tax to achieve the desired level of pollution. Instead, it auctions off tradable pollution permits, Each permit entities its owner to emit one ton of radioactive waste per day. To achleve the socially optimal quantity of pollution, the government auctions off 120 million pollution permits. Given this quantity of permits, the price for each permit in the market for pollution rights will be The previous analysis hinges on the government having good information regarding either the demand for pollution permits or the optimal level of pollution (or both), Given that the apgropriate polscy (tradable permits or corrective taxes) can depend on the avaliable information and the policy. goal, consider the following scenario. Imagine that new research supgests that if manufacturers in a particular city reduced their emissions to 30 million tons of waste per year, the air quality would improve dramatically. If this is all the information the government has, which solution to reduce pollution is appropriate? Check all that apply. Corrective taxes Tradable permits
Expert Answer
As an AI language model, I am not able to use the Graph input Tool. However, I can still provide some information that can help you answer the questio