(Solved): 6. Understanding the kinked demand curve modelHappyland is one of five amusement parks on Sunshine I ...
6. Understanding the kinked demand curve model
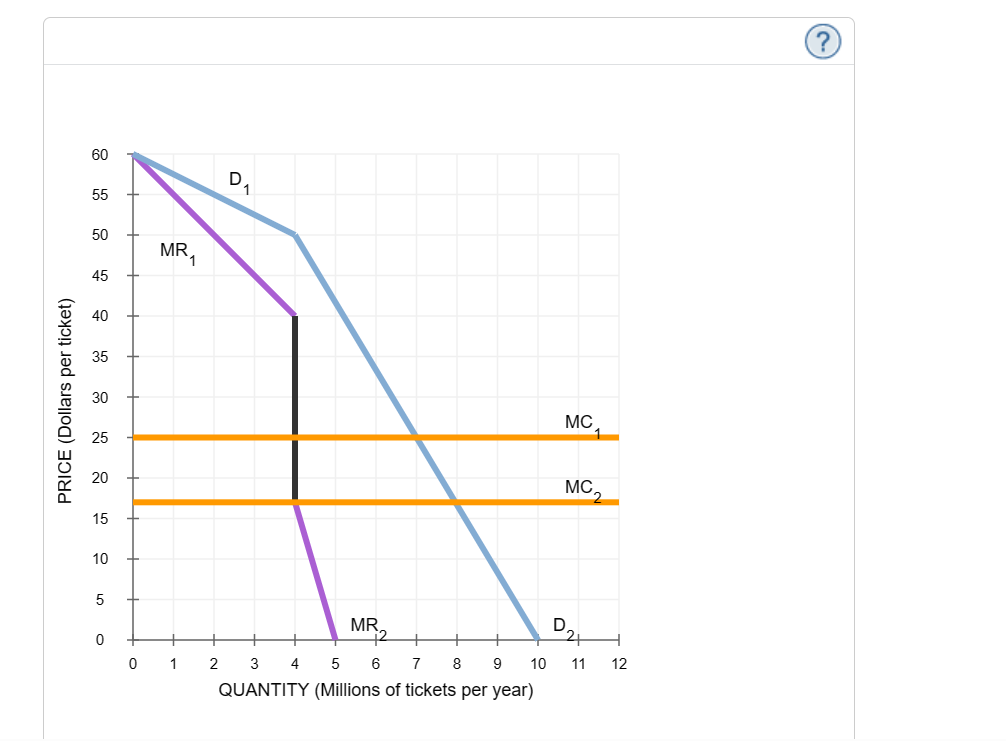
Happyland is one of five amusement parks on Sunshine Island. The following graph shows Happyland's kinked demand curve (D1?D2?1??2) and the resulting marginal revenue curve (MR1?MR2MR1?MR2). The graph also shows two possible marginal cost curves (MC1MC1 and MC2MC2).
Assume Happyland's marginal cost is represented by MC1MC1. Happyland will set a price of ($40/$50/ $25/$17) per ticket.
According to the kinked demand curve model, if one firm(raises/lowers) its price, other firms will not follow suit, but if one firm (raises/lowers) its price, other firms will do likewise to retain their market share. Therefore, if Happyland decreases its price to below the price you just found for Happyland, its competitors will (increase the price/ match the price decrease/ keep the price unchanged) .
The basic principle behind the kinked demand curve model explains why the D2?2 portion of the kinked demand curve is relatively( less/more) elastic than the D1?1 portion.
If Happyland's marginal cost decreased from MC1MC1 to MC2MC2 on the graph, Happyland would (not change its price/ decrease its price by $8/ increase its price by $ 10/ decrease its price by $ 10) .
Expert Answer
Answers:Price: $50 per ticket.Raises: If one firm raises its price, other firms will not follow suit...