Home /
Expert Answers /
Mechanical Engineering /
25-m3-hr-of-air-at-600-kpa-330-k-enters-a-well-insulated-horizontal-pipe-having-a-diameter-of-1-2-pa457
(Solved): 25 m3/hr of air at 600 kPa, 330 K enters a well-insulated, horizontal pipe having a diameter of 1.2 ...
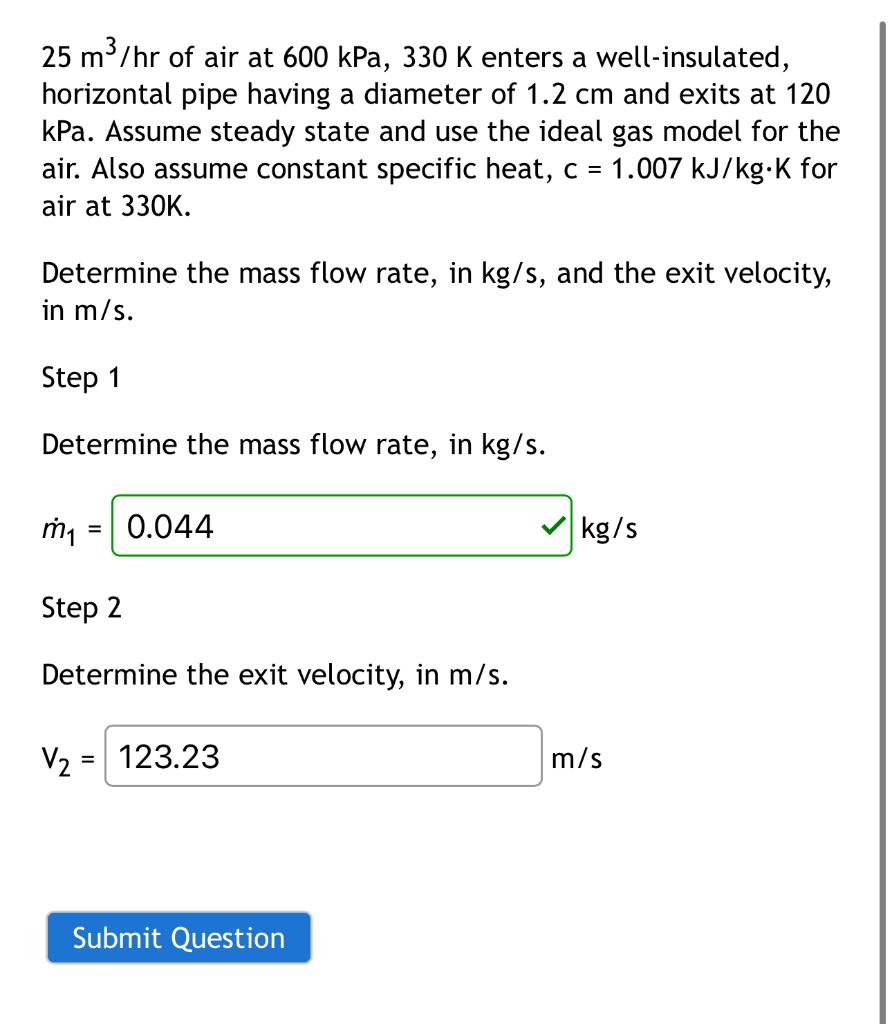
25 m3/hr of air at 600 kPa, 330 K enters a well-insulated, horizontal pipe having a diameter of 1.2 cm and exits at 120 kPa. Assume steady state and use the ideal gas model for the air. Also assume constant specific heat, c = 1.007 kJ/kg·K for air at 330K.
Determine the mass flow rate, in kg/s, and the exit velocity, in m/s.
of air at enters a well-insulated, horizontal pipe having a diameter of and exits at 120 . Assume steady state and use the ideal gas model for the air. Also assume constant specific heat, for air at . Determine the mass flow rate, in , and the exit velocity, in . Step 1 Determine the mass flow rate, in . Step 2 Determine the exit velocity, in .
Expert Answer
mass flow rate is 0.044 kg/s and the exit velocity is 94.37 m/s.Explanation:Using the ideal gas law, we can calculate the density of air at the inlet