Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemistry /
15-1-arrangement-of-the-periodic-table-according-to-the-highest-energy-sublevel-occupied-in-the-grou-pa491
(Solved): 15.1 Arrangement of the periodic table according to the highest-energy sublevel occupied in the grou ...
15.1
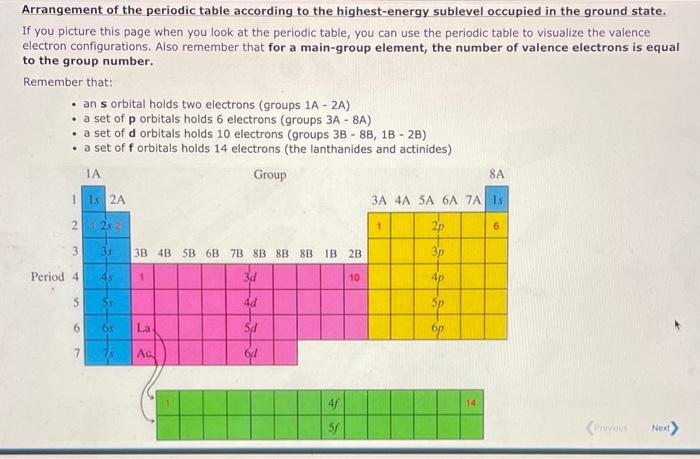





Arrangement of the periodic table according to the highest-energy sublevel occupied in the ground state. If you picture this page when you look at the periodic table, you can use the periodic table to visualize the valence electron configurations. Also remember that for a main-group element, the number of valence electrons is equal to the group number. Remember that: - an orbital holds two electrons (groups - ) - a set of orbitals holds 6 electrons (groups - ) - a set of d orbitals holds 10 electrons (groups ) - a set of orbitals holds 14 electrons (the lanthanides and actinides)
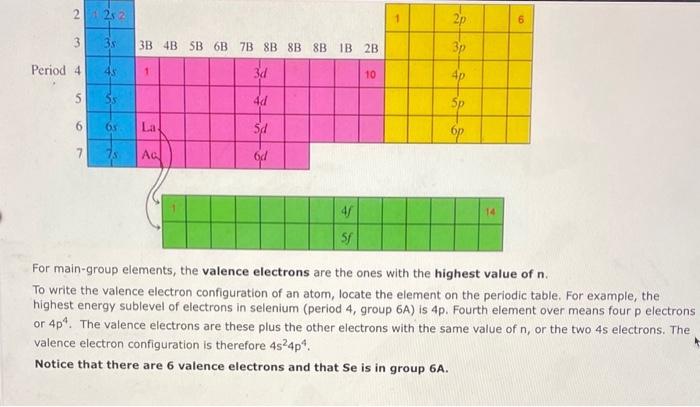
For main-group elements, the valence electrons are the ones with the highest value of . To write the valence electron configuration of an atom, locate the element on the periodic table. For example, the highest energy sublevel of electrons in selenium (period 4, group ) is . Fourth element over means four electrons or . The valence electrons are these plus the other electrons with the same value of , or the two electrons. The valence electron configuration is therefore . Notice that there are 6 valence electrons and that Se is in group .
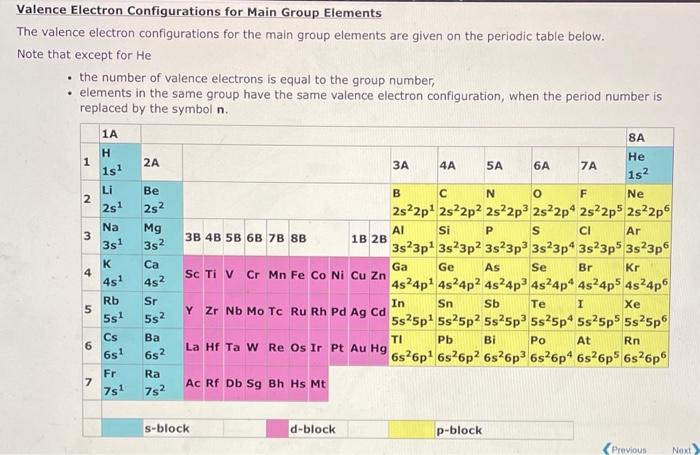
Valence Electron Configurations for Main Group Elements The valence electron configurations for the main group elements are given on the periodic table below. Note that except for He - the number of valence electrons is equal to the group number, - elements in the same group have the same valence electron configuration, when the period number is replaced by the symbol .
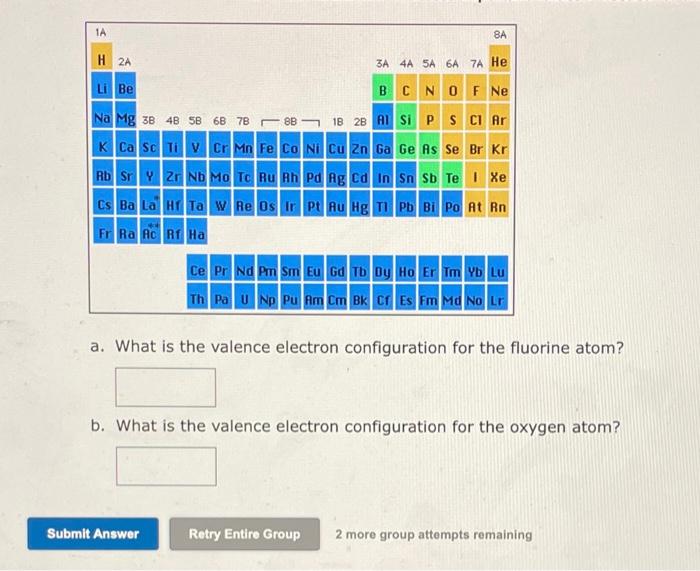
a. What is the valence electron configuration for the fluorine atom? b. What is the valence electron configuration for the oxygen atom? 2 more group attempts remaining
a. What is the valence electron configuration for the fluorine atom? b. n for the oxygen atom? mpts remaining