(Solved): 11. Select the option that best describes the bonding or interaction(s) between a viral lectin ...
11.
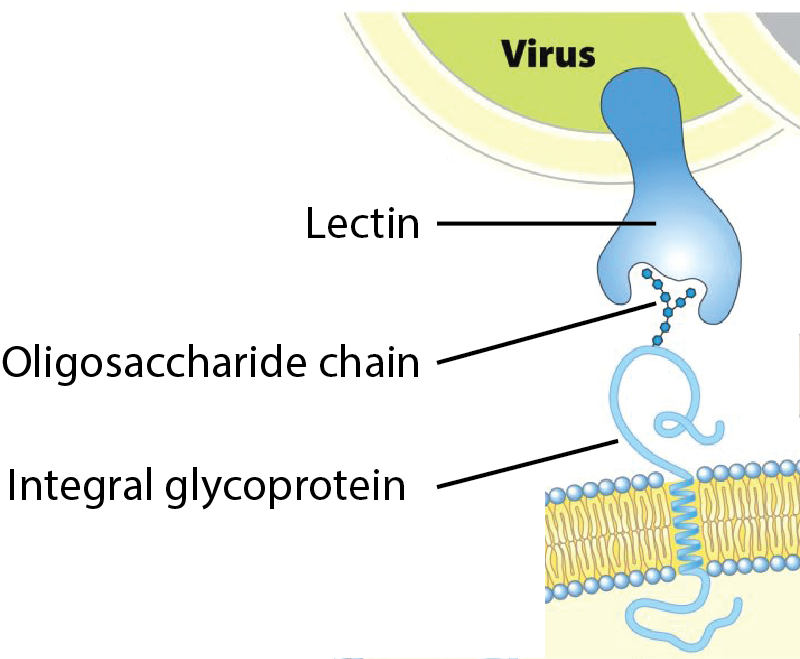
Select the option that best describes the bonding or interaction(s) between a viral lectin and its carbohydrate target. In this case the carbohydrate target is part of an integral glycoprotein found on the surface of a cell. See the image below that illustrates this situation.
|
Ionic bonding would occur between the carbohydrate and the lectin following deprotonation of the OH groups on the carbohydrate. |
||
|
Hydrophobic interaction holds the protein to the carbohydrate due to non-polar residues on the protein binding with the OH groups on the carbohydrate. |
||
|
Covalent bonding occurs through a condensation reaction between the OH groups on the carbohydrate and cysteine residues on the lectin. |
||
|
The lectin phosphorylates the free OH groups found on the carbohydrate. |
||
|
Hydrogen bonding occurs between charged groups on the protein and hydroxyl groups on the carbohydrate. |
Expert Answer
Hydrogen bonding occurs between charged groups on the protein and hydroxyl