Home /
Expert Answers /
Biology /
1-simple-squamous-epithelium-2-stratified-squamous-epithelium-3-simple-cuboidal-epithelium-4-tr-pa325
(Solved): 1. Simple squamous epithelium 2. Stratified squamous epithelium 3. Simple cuboidal epithelium 4. Tr ...
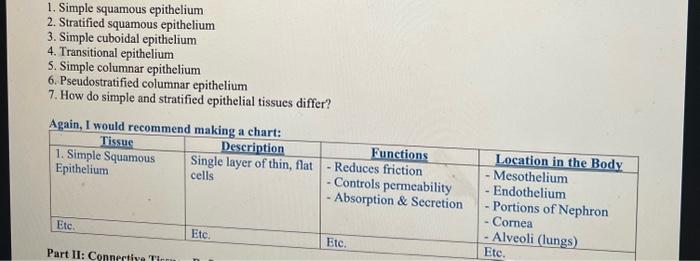

1. Simple squamous epithelium 2. Stratified squamous epithelium 3. Simple cuboidal epithelium 4. Transitional epithelium 5. Simple columnar epithelium 6. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium 7. How do simple and stratified epithelial tissues differ?
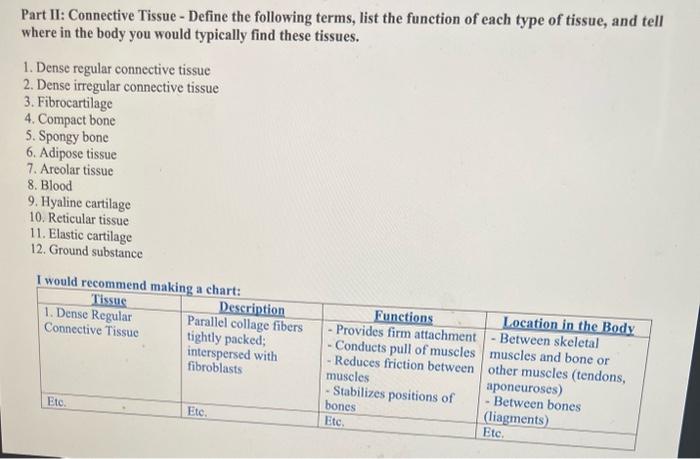
Part II: Connective Tissue - Define the following terms, list the function of each type of tissue, and tell where in the body you would typically find these tissues. 1. Dense regular connective tissue 2. Dense irregular connective tissue 3. Fibrocartilage 4. Compact bone 5. Spongy bone 6. Adipose tissue 7. Areolar tissue 8. Blood 9. Hyaline cartilage 10. Reticular tissue 11. Elastic cartilage 12. Ground substance
12. Classify each of the above tissues into the correct subtype of connective tissue: loose, dense, fluid, or supporting. 13. What is a ground substance? 14. Differentiate between elastic fibers, reticular fibers, and collagen fibers.
Expert Answer
ans. answer of this question as you required format-ans 7.Difference between simple and stratified are -1. Structure:- Simple epithelium: It consists of a single layer of cells that are tightly packed together. The cells are in direct contact with the basement membrane, which separates the epithelium from the underlying connective tissue.- Stratified epithelium: It consists of multiple layers of cells stacked on top of each other. Only the basal layer of cells is in contact with the basement membrane, while the upper layers of cells are farther away from the basement membrane.2. Function:- Simple epithelium: It is involved in functions such as absorption, secretion, and diffusion. The single layer of cells allows for efficient exchange of substances between the epithelium and the underlying tissues.- Stratified epithelium: It provides protection against mechanical stress, abrasion, and chemical damage. The multiple layers of cells provide a stronger barrier to protect underlying tissues.3. Location:- Simple epithelium: It is found in areas where absorption, secretion, and diffusion are essential. Examples include the lining of the intestines, kidney tubules, and air sacs of the lungs.- Stratified epithelium: It is typically found in areas that require protection, such as the outer layer of the skin (epidermis), lining of the mouth, esophagus, and urinary bladder.In summary, simple epithelium is a single layer of cells that facilitates exchange functions, while stratified epithelium is a multilayered tissue that provides protection.